Executive Summary
Astar Network is a decentralized blockchain platform designed to facilitate Web3 innovations. It is compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) and WebAssembly environments, fostering seamless interoperability between these ecosystems. Developers can secure incentives through the Build2Earn program, which rewards the creation of decentralized applications. Astar’s primary objective is to establish a highly scalable network that underpins a global Web3 vision.
Notably, Astar Network operates in tandem with prominent blockchain networks such as Ethereum, Polkadot, and Cosmos. This collaborative approach promotes the unfettered exchange of assets and information across diverse blockchain ecosystems. The project benefits from backing by a consortium of well-established organizations within the cryptocurrency industry.
Current Metrics
FDV-$408M
TVL- $27M
Market Cap- $264M
Overview
The ever-expanding user base in the cryptocurrency space necessitates the evolution of dApps towards mainstream adoption. Consequently, there is an escalating demand for dApps that offer cost-efficiency, expeditious performance, and enhanced user experiences. Astar addresses this need by providing developers with a platform prioritizing swifter, more cost-effective, and highly scalable development. Moreover, Astar offers additional layers of optimization, including Plasma and zero-knowledge (ZK) rollups, designed to enhance operational efficiency significantly. Plasma streamlines transaction management beyond the primary chain, accelerating the process. Additionally, Astar facilitates cross-chain interoperability for Web 3.0 applications, leveraging the capabilities of Polkadot.
Astar is a prominent platform for developing decentralized applications (dApps) within the Web 3.0 ecosystem, specifically geared towards creating smart contracts. This platform boasts compatibility with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) and WebAssembly (WASM) virtual machines, with EVM representing a versatile computational engine supporting many executable projects. At the same time, WASM serves as a portable compilation target, facilitating deployment on the web through various programming languages.
Astar has solidified its reputation as a preferred smart contract platform for Web 3.0 developers thanks to its compatibility with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) and WebAssembly (WASM). The project’s overarching goal is to enhance efficiency, encompassing both cost-effectiveness and speed, for developers operating within the increasingly crowded blockchain landscape. Through the introduction of dApp staking, users are granted the ability to back projects tailored to their preferences, as opposed to participating in the network’s security staking.
Key Highlights
- Cross-Virtual Machine (XVM): Interoperability between EVM and Wasm, supporting diverse developers.
- Scalability: Overcomes traditional blockchain limitations, supports multichain smart contracts, and is future-proof.
- Interoperability: Advanced framework backed by Polkadot’s security and XVM for seamless dApp interactions.
- dApp Staking: Unique mechanism offering compensation for dApp developers, promoting quality dApp creation.
- Proxy Accounts: Provides various permissions to delegate accounts, ensuring high security.
- Consensus: A high-performance blend of PoS and PoW, ensuring security and scalability.
- XCM: Messaging protocol allowing diverse blockchain communication, particularly in the Polkadot ecosystem.
How does it work?
The Astar Network operates on a dual-layer architecture that enhances scalability and performance. The first layer, often called the base layer, is a Layer 1 blockchain meticulously constructed using the Substrate blockchain framework, known for its robustness and flexibility. The second layer represents a scaling solution ingeniously harnessed through utilizing the Optimistic Virtual Machine (OVM), a groundbreaking innovation pioneered by the Plasma Group.
Astar distinguishes itself by allowing developers to harness the capabilities of the OVM module, enabling them to tailor their scaling solutions according to their specific requirements. This flexibility empowers developers to seamlessly integrate their application layers into the foundational infrastructure of Astar by leveraging technologies such as Plasma and Zero-Knowledge (ZK) rollups.
Notably, Layer 2 solutions within the Astar ecosystem are entrusted with the vital responsibilities of data storage and the commitment to state transitions, thus optimizing the overall efficiency and performance of the Astar base layer. This two-tiered approach is pivotal in addressing the growing demands of a rapidly evolving blockchain landscape.
Astar Tokenomics
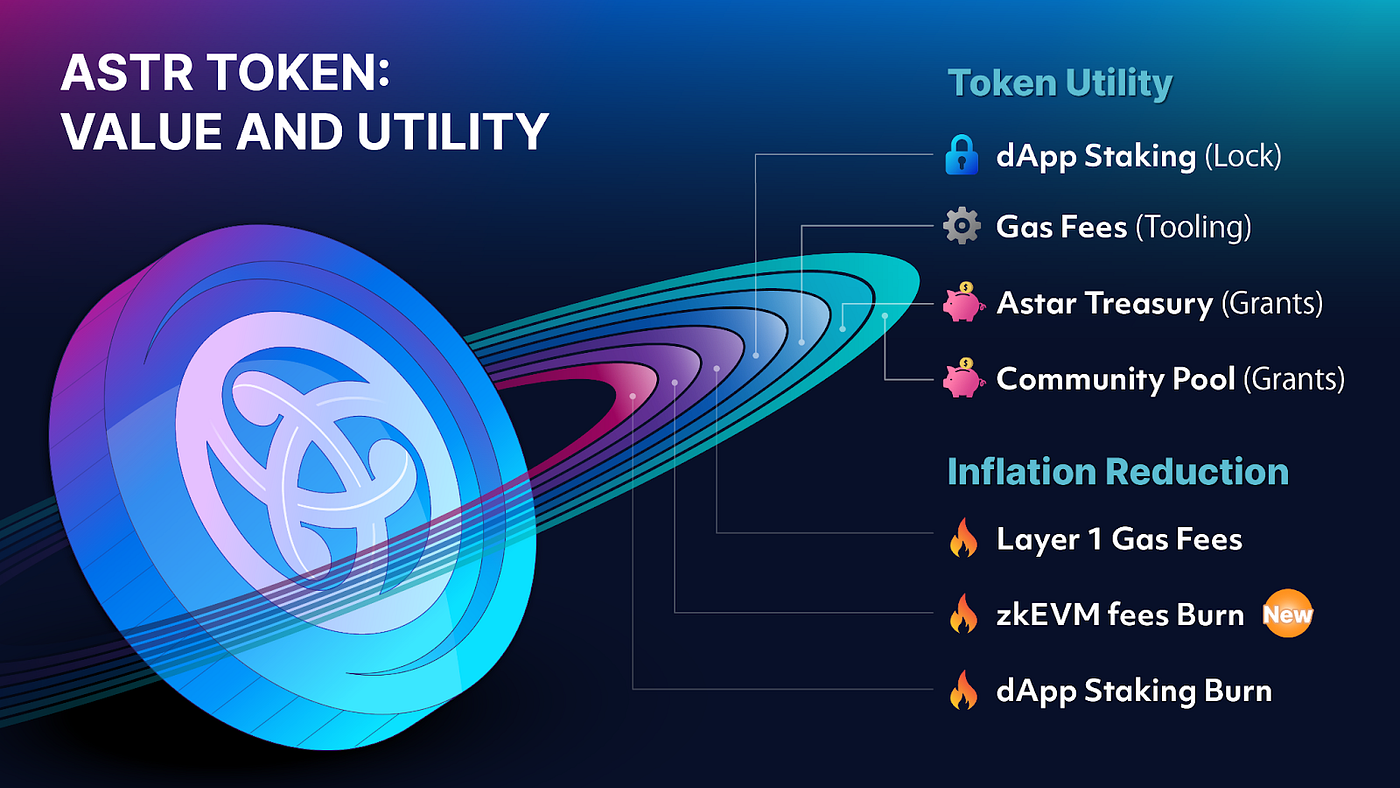
The $ASTR token, as the native token of the Astar platform, holds a pivotal role within the Astar network, functioning as a versatile utility token with various key roles:
- dApps Staking: Astar Network has innovatively introduced a unique form of staking exclusive to its ecosystem. $ASTR token holders can stake their tokens on decentralized applications (dApps) and, in return, receive rewards. This incentivizes active participation and engagement within the Astar ecosystem. Furthermore, developers contributing to the network’s growth by creating smart contracts or enhancing its infrastructure earn $ASTR tokens.
- Network Staking: $ASTR token holders can engage in network staking by committing their tokens to become validators. This proactive involvement allows them to earn rewards while contributing to the security and integrity of the Astar Network.
- Fees: The $ASTR token is accepted as a means of payment for covering on-chain transaction fees. Its utilization in this capacity facilitates seamless and efficient transactions within the network.
- Layer 2 Deposits: Astar, operating as a Layer 1 platform, supports Layer 2 implementations. Layer 2 applications, in line with this support, initiate $ASTR token deposits within Layer 1 smart contracts. These deposits are the foundation for creating and operating Layer 2 applications, fostering a more scalable and optimized network.
- On-chain Governance: $ASTR token holders are actively engaged in the governance of the Astar Network. They exercise their voting rights to make decisions on various proposals, contributing to the evolution and improvement of the network’s protocols and policies.
Reduced Inflation
Network activity in the Astar Tech Stack actively reduces the $ASTR token inflation. Three fundamental mechanisms are employed to limit $ASTR growth:
- In the Astar Substrate environment, 80% of the $ASTR used for gas fees is burned.
- In the Astar zkEVM environment, network activity and ETH earned from Sequencers are used for $ASTR buyback and burning.
- The new dApp staking model includes burning unused rewards.
These actions collectively work to maintain controlled $ASTR token inflation.
Team and Investors

Astar was established in 2019 under the visionary leadership of Sota Watanabe. Complementing Astar’s initiatives, Startale Labs, a sister organization to the Astar Foundation, has already forged significant partnerships and relationships within Japan. Noteworthy collaborations include prominent entities such as JR Kyushu, the nation’s largest train company, Sony Network Communications, and Toyota. Leveraging the success and influence cultivated through these associations, Watanabe and his team are determined to propel Web3 into a global phenomenon. Their strategic approach and vision extend far beyond regional boundaries, embodying a commitment to realizing the full potential of decentralized technologies on a worldwide scale.
Conclusion
Astar Network emerges as a significant contributor to the advancement of interoperability and the widespread adoption of diverse use cases within the blockchain industry. By fostering an environment of inclusivity, it creates fresh opportunities for developers across the blockchain landscape, irrespective of their chosen chain or cryptocurrency. This concerted effort plays a pivotal role in expediting the development and realization of Web 3.0. It has positioned itself as a vanguard for innovation within the Web 3.0 arena. Astar is an attractive hub for emerging projects, offering a compelling blend of technical capabilities and enticing financial incentives.
The project’s governance structure is poised for a gradual transition towards decentralization, culminating in establishing a Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) featuring direct on-chain voting. This evolution underscores Astar’s commitment to community-driven decision-making, further solidifying its pivotal role in shaping the future of Web 3.0.
| Fundamental Analysis | |||||
| Assessment | |||||
| Problem | Significant, long-term problem | 3 | |||
| Solution | Distinct, defensible solution | 3 | |||
| Market Size | Large market, significant growth potential | 3 | |||
| Competitors | Saturated market, dominant players entrenched | 1 | |||
| Unique Value Proposition | Clear differentiation and value for customers | 3 | |||
| Current Traction | Solid traction, user engagement and retention growing | 3 | |||
| Unit Economics | Positive unit economics, with plans for further improvement | 3 | |||
| Tokenomics | Solid token strategy, aligns with user incentives | 3 | |||
| Product Roadmap | Clear roadmap, innovative and achievable milestones | 3 | |||
| Business Model | Proven business model with clear path to profitability | 3 | |||
| Go-to-Market Strategy | Basic GTM strategy, lacks detail or differentiation | 2 | |||
| Regulatory Risks | Minimal regulatory risk, strong mitigation and adaptability | 4 | |||
| Total | 70.83% | ||||