Executive Summary
Eclipse is a Layer 2 platform designed to significantly enhance scalability and performance for blockchain applications by utilizing the Solana Virtual Machine (SVM). It addresses the scalability limitations of Ethereum and other Layer 1 networks, providing users and developers with faster and more cost-effective transactions. By integrating the SVM, Eclipse leads the way in advancing scalability and performance within the blockchain ecosystem.
About the Project
Vision – Eclipse envisions itself as a pioneering Layer 2 solution on Ethereum, leveraging the Solana Virtual Machine (SVM) to redefine the blockchain landscape. By integrating Ethereum’s trusted settlement capabilities with the unparalleled speed and scalability of SVM, the Eclipse Mainnet is positioned to be a leading force in delivering high-performance, secure, and scalable blockchain solutions.
Problem – The development and widespread adoption of cryptocurrency have been significantly impeded by the scarcity of fast, truly decentralized open-source projects. Slow transaction speeds and high fees have further complicated the effective use of cryptocurrencies for everyday payments, deterring both new and existing users. While Solana has emerged as a formidable competitor to Ethereum, recognized for its exceptional speed, it lacks compatibility with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), limiting its interoperability within the broader blockchain ecosystem.
In response to these challenges, several Layer 2 solutions have been introduced, aiming to enhance transaction speeds and reduce costs. However, despite their potential, they still need to match the scale, performance, or community adoption that Solana has achieved. The need for a solution that combines speed, scalability, and broad compatibility remains critical for advancing the crypto landscape and enabling seamless, widespread adoption.
Solution – Eclipse Network, an Ethereum SVM Layer 2 solution, seamlessly integrates the strengths of both Ethereum and Solana, offering a high-performance execution environment paired with unmatched liquidity. Designed to overcome the scalability challenges inherent in Ethereum and other Layer 1 networks, Eclipse enables faster and more cost-effective transactions for users and developers.
As the demand for decentralized applications (dApps) continues to rise, existing blockchain networks have struggled with high transaction fees and slow processing times, hindering their ability to scale. Eclipse tackles these issues by offloading computations from the main chain to a secondary layer, ensuring that transactions are processed swiftly and affordably while maintaining the robust security and decentralization of the underlying blockchain.
Eclipse’s innovative approach is grounded in a ‘best of all worlds’ philosophy, effectively addressing the scalability trilemma without compromising on any core aspect. By combining the trusted security of Ethereum with the rapid transaction speeds and efficiency of Solana, Eclipse is poised to become a pivotal solution in the blockchain ecosystem, empowering developers to create more powerful dApps and users to experience a seamless, efficient blockchain environment. As the network evolves, it is set to redefine the standards for performance, scalability, and interoperability in the decentralized world.
What is Solana VM?
The Solana Virtual Machine (SVM) is an advanced execution environment engineered to enable rapid, scalable, and efficient transaction processing on the Solana blockchain. Leveraging Solana’s unique architecture, the SVM is renowned for its ability to handle parallel transaction processing, resulting in exceptionally high throughput rates. This capability sets Solana apart as one of the fastest and most efficient blockchains in the industry.
The SVM is also designed to support smart contracts and decentralized applications, offering developers a robust platform to build high-speed blockchain solutions. With a strong emphasis on performance, the SVM not only enhances scalability but also significantly reduces transaction costs, making it an attractive choice for both developers and users seeking swift, cost-effective on-chain interactions. Beyond its technical prowess, the SVM plays a crucial role in Solana’s appeal by providing the necessary infrastructure to support a growing ecosystem of decentralized applications. By ensuring that transactions are processed quickly and efficiently, the SVM contributes to the overall user experience, enabling seamless and reliable interactions on the blockchain.
EVM compatibility using Neon Stack
Eclipse has formed a strategic partnership with Neon Stack to introduce Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) compatibility to the Eclipse network. This integration enables Solidity developers to seamlessly deploy Ethereum-native dApps on Eclipse using their existing codebase. Neon Stack, a standardized development stack, facilitates EVM compatibility for SVM-based blockchain networks and will now be implemented on the Eclipse SVM Layer 2.
The Neon Stack incorporates Neon EVM smart contracts and Neon Proxy, offering a proven solution for developers. With this integration, developers on Eclipse can continue writing smart contracts in familiar languages like Solidity and Vyper, utilize popular Ethereum tools, maintain Ethereum RPC API compatibility, and build around Ethereum accounts, signatures, and token standards—all while benefiting from the enhanced performance of the SVM. Users, in turn, will gain access to EVM-based dApps they frequently use, but within a more efficient execution environment. This enhances blockchain interoperability and scalability while simplifying infrastructure implementation for developers looking to leverage SVM capabilities within Ethereum-native dApps. By enabling both SVM and EVM developers to build on Eclipse while retaining their preferred development environments, Eclipse is further promoting the integration and harmony between the Solana and Ethereum ecosystems.
How does it Work?
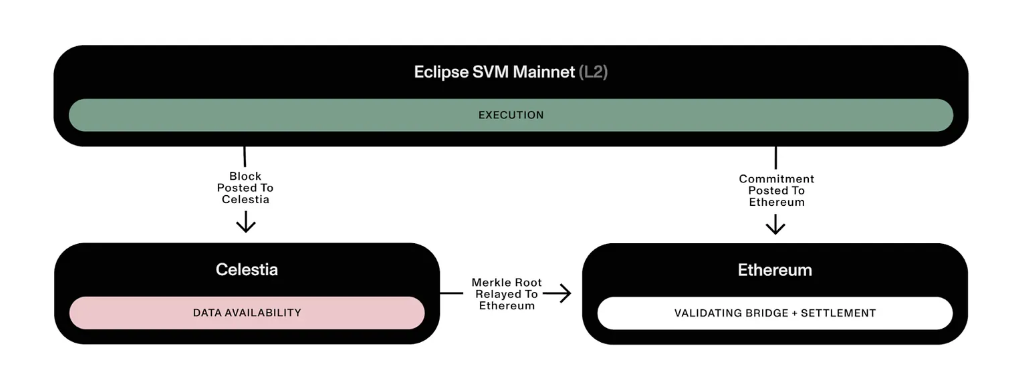
Eclipse Mainnet represents Ethereum’s first general-purpose Layer 2 solution centered around the Solana Virtual Machine (SVM). Designed with a modular architecture, Eclipse aspires to be the fastest and most versatile Layer 2 network powered by SVM. The project’s innovative structure integrates Ethereum as the settlement layer, Celestia for data availability, RISC Zero for zero-knowledge fraud proofs, and Solana’s SVM as the execution environment. Below is an overview of the key components based on the official description:
Settlement Layer — Ethereum:
Eclipse uses Ethereum as its settlement layer, leveraging an embedded verification bridge. This architecture allows Eclipse to settle transactions on Ethereum, utilize ETH for gas fees, and submit fraud proofs directly on the Ethereum network, ensuring a secure and decentralized foundation.
Execution Layer — Solana Virtual Machine (SVM):
At the core of Eclipse’s execution environment is the Solana Virtual Machine (SVM), specifically a high-performance fork of the Solana Labs client (v1.17). The SVM is designed to handle rapid and scalable transaction processing, making it an ideal execution layer for this modular Layer 2 solution.
Data Availability Layer — Celestia:
To achieve scalable data availability, Eclipse publishes data to Celestia, a specialized data availability layer. This integration ensures that data is readily accessible and verifiable, supporting the high throughput and efficiency that Eclipse aims to deliver.
Proof Mechanism — RISC Zero:
Eclipse employs RISC Zero to generate zero-knowledge (ZK) fraud proofs, eliminating the need for intermediate state serialization. This advanced proof mechanism enhances security and trust within the network while maintaining optimal performance.
Communication Protocol — IBC:
Eclipse uses the Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC) protocol, a standard developed by the Cosmos ecosystem, to enable seamless bridging with non-Eclipse chains. This ensures interoperability and connectivity across different blockchain networks.
Cross-Chain Protocol — Hyperlane:
In collaboration with Hyperlane, Eclipse integrates a permissionless interoperability solution tailored for blockchains based on the Solana Virtual Machine (SVM). This cross-chain protocol enhances Eclipse’s ability to communicate and interact with other networks, further expanding its versatility.
Eclipse’s architecture exemplifies a “best of all worlds” approach, combining the strengths of Ethereum, Solana, Celestia, RISC Zero, IBC, and Hyperlane to create a powerful, scalable, and secure Layer 2 solution.
Market Analysis
Since its inception, blockchain technology has witnessed remarkable growth, achieving a valuation of $2.6 trillion. Optimistic projections indicate continued expansion, supported by increasing government adoption, further strengthening this positive outlook. In the broader cryptocurrency industry, the most influential protocols are those valued in the billions of dollars, reflecting the profound impact of this technology on global markets. Numerous Layer 2 solutions have emerged, propelling the evolution of blockchain technology forward and addressing the scalability challenges that earlier networks faced.
Modular blockchains are positioned as the future of this technology, offering unmatched scalability, flexibility, and efficiency. Unlike monolithic blockchains, where all functions are consolidated within a single layer, modular blockchains divide essential components such as data availability, consensus, and execution into distinct layers. This architectural innovation allows each layer to specialize and optimize its performance independently, ensuring that no single aspect of the system is a bottleneck. The ability to separate and optimize these functions empowers developers to build more robust and adaptable networks, supporting a wide range of applications and use cases.
As the blockchain ecosystem continues to mature, modular blockchains are expected to play a pivotal role in addressing the limitations of traditional architectures, paving the way for greater adoption across industries. A prime example of this trend is Celestia, which has gained significant traction and adoption, demonstrating the practical benefits of modular design in real-world applications. The success of such projects underscores the growing recognition that modular blockchains are not just an innovation but a necessity for the future scalability and sustainability of blockchain technology.
USP -Eclipse offers access to Ethereum, the most economically secure and attack-resistant settlement layer, with its extensive user base and liquidity. It provides superior speed, security, and scalability, making it ideal for deploying powerful applications. Eclipse optimizes the execution environment to the fullest extent by enhancing the Solana Virtual Machine (SVM) with hardware acceleration, pushing the boundaries of parallel execution to achieve maximum performance.
Competitors:
Rome – Rome is engineered to integrate Solana’s capabilities into Ethereum-based services by being a shared sequencer. This will enable Ethereum rollups to leverage Solana as a shared sequencer, accelerating transaction confirmations, improving privacy and scalability, and reducing blockchain costs. The Rome Protocol will facilitate using Solana’s existing validators as shared sequencers for transactions, state maintenance, and transaction publication. This initiative aims to transform Solana’s capacity of over 50,000 transactions per second (TPS) into a robust infrastructure for Ethereum rollups. Additionally, it ensures atomic composability, with transactions being confirmed on Solana before their submission to Ethereum.
Team

Neel Somani, the founder of Eclipse, having previously served as a software developer at Airbnb and a quantitative researcher at Citadel. Following allegations of sexual misconduct made by several users on X, Somani resigned from his position at the company.
In the wake of Somani’s departure, Eclipse Labs quickly moved to appoint Vijay Chetty, the former Chief Growth Officer, as its new CEO. Chetty’s appointment marks a pivotal moment for the company, as he brings over a decade of crypto-native experience and leadership to the role. His impressive background includes key positions at Uniswap Labs, dYdX Trading, and Ripple Labs, where he played significant roles in driving growth and innovation. Additionally, his investment experience at BlackRock adds a layer of financial acumen that is expected to guide Eclipse Labs through its next development phase.
Investors

Eclipse recently in March, secured $50 million in Series A funding, co-led by Placeholder and Hack VC, bringing its total capital raised to $65 million. The funding round attracted participation from prominent investors such as Polychain Capital, Delphi Digital, Maven 11, DBA, Apollo-managed funds, Fenbushi Capital, and ParaFi Capital. Strategic investments also came from Flow Traders, GSR, Auros, and OKX Ventures.The round was further bolstered by contributions from notable researchers and builders who participated as angel investors. Among them were Barnabé Monnot of the Ethereum Foundation, John Adler of Celestia Labs, Austin Federa of the Solana Foundation, ZachXBT, and Meltem Demirors. This diverse group of investors highlights the broad industry support and confidence in Eclipse’s vision and its potential to drive innovation in the blockchain space.
Conclusion
Eclipse is a groundbreaking platform designed to tackle the scalability challenges encountered by Ethereum and other Layer 1 networks. It delivers exceptional speed, performance, and security, making it an ideal solution for a broad spectrum of use cases and applications. Built as a Layer 2 network for the future, Eclipse offers superior capabilities that empower developers to create robust and scalable applications.
With over 13,000 dApps, billions of dollars in the Ethereum ecosystem, and thousands of EVM developers, the potential for cross-chain growth is immense. Eclipse Labs recognizes that developers seek to preserve their expertise in EVM, maintain familiarity with existing tools, and continue accessing Ethereum’s liquidity and user base. At the same time, they require the speed and throughput necessary to scale, similar to the high-performance environment found on Solana. Eclipse addresses these needs, offering a platform that bridges the gap between Ethereum’s extensive ecosystem and the demand for enhanced performance. As the blockchain landscape continues to evolve, the need for solutions that combine the strengths of different ecosystems becomes increasingly clear. Eclipse stands at the forefront of this transformation, providing a seamless integration that allows developers to leverage their existing knowledge while accessing cutting-edge technology. By delivering unparalleled speed, security, and scalability, Eclipse not only meets the current demands of the industry but also sets the stage for future innovations. It is a platform that not only solves present challenges but also paves the way for a more interconnected and efficient blockchain ecosystem.
| Fundamental Analysis | |||||
| Assessment | |||||
| Problem | Significant, long-term problem | 3 | |||
| Solution | Distinct, defensible solution | 3 | |||
| Market Size | Large market, significant growth potential | 3 | |||
| Competitors | High competition, but room for differentiation | 2 | |||
| Unique Value Proposition | Clear differentiation and value for customers | 3 | |||
| Current Traction | Early traction, user engagement starting to grow | 2 | |||
| Unit Economics | Positive unit economics, with plans for further improvement | 3 | |||
| Tokenomics | No clear token strategy or poorly conceived strategy | 1 | |||
| Product Roadmap | Clear roadmap, innovative and achievable milestones | 3 | |||
| Business Model | Proven business model with clear path to profitability | 3 | |||
| Go-to-Market Strategy | Solid GTM strategy, clear target market and channels | 3 | |||
| Regulatory Risks | Minimal regulatory risk, strong mitigation and adaptability | 4 | |||
| Total | 68.75% | ||||