Executive Summary

ether.fi is a decentralized, non-custodial delegated staking protocol featuring a Liquid Staking Derivative token. A key feature of ether.fi is the empowerment of stakers, who maintain control over their keys. The protocol also facilitates the establishment of a node services marketplace, enabling stakers and node operators to enroll nodes to provide infrastructure services, with resulting revenues shared among stakers and node operators. Under the ether.fi framework, stakers maintain control over their keys and retain custody of their ETH while delegating staking to a node operator, significantly reducing their risk exposure.
About the Project
ether.Fi offers two critical differentiators in its approach to staking. Firstly, stakers on Ether.fi generate and retain control over their own staked ETH keys. This contrasts with many other delegated staking protocols where stakers typically deposit their ETH and are matched with a node operator who then generates and holds the staking credentials. While some protocols can be configured to be non-custodial, in practice, this often results in a custodial or semi-custodial setup, introducing significant and opaque counterparty risks for the staker.
Secondly, ether.fi mints an NFT (Non-Fungible Token) for every validator launched through its platform. These NFTs represent the 32 ETH staked and store essential metadata about the validator, including the client it runs, its geographical location, the node operator, and any node services it utilizes. Additionally, these NFTs play a crucial role in creating the Liquid Staking Derivative token eETH, which is minted from a liquidity pool containing these NFTs.
Overall, ether.fi approach empowers stakers by allowing them to retain custody of their ETH while still delegating staking responsibilities to a node operator. This significantly reduces the risk exposure for stakers. Furthermore, using NFTs adds a programmable layer to the staking infrastructure, potentially enhancing its capabilities through integration with EigenLayer in the future.
ether.fi offers stakers a unique framework that allows them to maintain control over their keys and retain custody of their ETH while delegating staking to a node operator, effectively reducing their risk exposure. A notable feature of ether.fi is its generation of an NFT for each validator launched via the protocol. The Liquid Staking Derivative token, eETH, is minted from a liquidity pool that includes these NFTs. These NFTs manage the 32 ETH staked and contain metadata related to the validator, such as the client it operates, its geographical location, the node operator, and any associated node services. These NFTs have the potential to be leveraged to create a programmable layer atop staking infrastructure, with expected enhanced capabilities through integration with EigenLayer in the future.
- Native Restaking – Native restaking in ether.fi offers increased freedom and potentially higher rewards, allowing users to earn staking and restaking yields through EigenLayer, leveraging their existing ETH holdings.
- Decentralization – Decentralization is a core focus of ether.fi, exemplified by Operation Solo Staker, aims to further decentralize Ethereum by launching nodes across diverse geographical locations.
- Control – A key feature of ether.fi is its emphasis on user control: it is the only protocol where stakers maintain control over their keys. This reduces the counterparty risk associated with node operators and the protocol itself.
- DeFi ecosystem – ether.fi fosters a thriving ecosystem around its native token, eETH, designed for use in decentralized finance (DeFi). The protocol is actively partnering with various DeFi projects to enhance the utility of eETH within the broader ecosystem.
Market Analysis
EigenLayer has pioneered a resource management approach to decentralized staking through its Restaking protocol. EigenLayer’s protocol, launched last June, introduced a “restaking” system to Ethereum, allowing blockchain apps and networks to leverage Ethereum’s security without building their proof-of-stake networks.
This innovation utilizes Liquid Restaking Tokens (LRT), a flexible form of staked tokens, to maximize the value extracted from staking activities. This approach benefits stakers, other networks, and the restaking protocol itself. Restaking has emerged as a prominent narrative in the blockchain space, focusing on capital efficiency by allowing users to stake tokens on the main blockchain and other protocols simultaneously. This approach enables users to secure multiple networks concurrently, offering additional rewards for securing different protocols.
The concept of restaking is gaining traction, with many projects exploring ways to leverage restaking resources or participate as restaking resource providers. Projects like Puffer Finance and Swell have come into the market, with the TVL almost $1B.
Traction
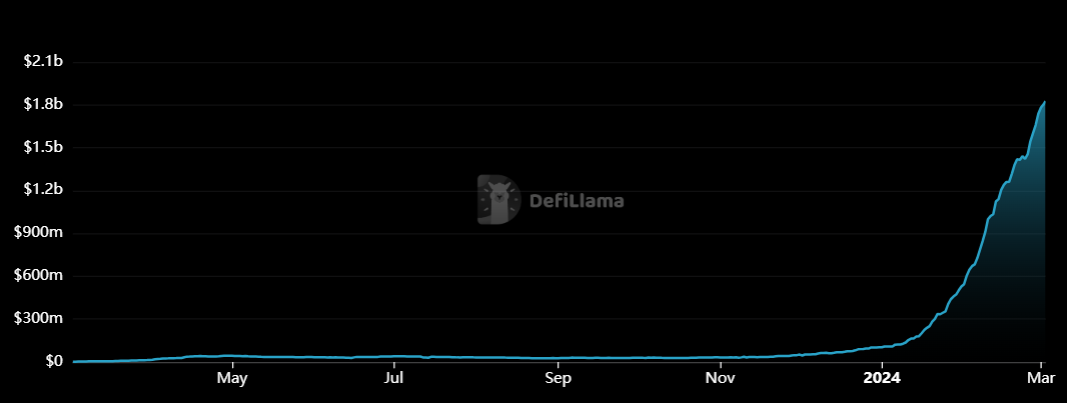
Ether.fi has distinguished itself in the restaking protocol landscape with its unique offerings. As a leading protocol in this space, it boasts a Total Value Locked (TVL) of $1.87 billion, showcasing strong adoption and a promising future.
Investors

ether.fi Team
Mike Silagadze, the CEO and founder of ether.fi, brings a wealth of experience from the crypto space to his role. Prior to founding ether.fi, he managed a crypto fund. He is supported by a talented team that has collectively delivered exceptional results thus far.
Conclusion
ether.fi stands out as the sole protocol that enables stakers to maintain control of their keys while delegating staking responsibilities, offering a distinctive solution for those seeking to participate in staking. Through ether.fi, stakers retain control over their keys and ETH while entrusting staking operations to a node operator, significantly reducing their risk exposure. With its unique offerings, substantial traction, and a sizable market, ether.fi appears poised for a promising future.
| Fundamental Analysis | |||||
| Assessment | |||||
| Problem | Significant, long-term problem | 3 | |||
| Solution | Distinct, defensible solution | 3 | |||
| Market Size | Large market, significant growth potential | 3 | |||
| Competitors | Emerging market with few strong competitors | 3 | |||
| Unique Value Proposition | Clear differentiation and value for customers | 3 | |||
| Current Traction | High traction, strong user growth and retention | 4 | |||
| Unit Economics | Positive unit economics, with plans for further improvement | 3 | |||
| Tokenomics | No clear token strategy or poorly conceived strategy | 1 | |||
| Product Roadmap | Basic roadmap, lacks detail or innovative features | 2 | |||
| Business Model | Proven business model with clear path to profitability | 3 | |||
| Go-to-Market Strategy | Basic GTM strategy, lacks detail or differentiation | 2 | |||
| Regulatory Risks | Minimal regulatory risk, strong mitigation and adaptability | 4 | |||
| Total | 70.83% | ||||