io.net is a decentralized GPU network created to offer scalable and cost-effective computing power for machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) applications. This initiative aims to tackle the global shortage of GPU capacity, which is essential for training and deploying AI models that consolidates GPUs from various underutilized sources into a Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Network (DePIN), enabling scalable and customizable computing power for a variety of tasks, including
About the Project
Vision – io.net aims to create a globally accessible, decentralized cloud computing network that offers affordable, flexible, and permissionless access to computing resources. By aggregating GPUs from underutilized sources, including independent data centers, idle cryptocurrency mining farms, and individual consumers, io.net can deliver computing power at a cost up to 90% lower than that of centralized cloud providers.
Problem – Despite the rising demand for computing power in AI and machine learning, many independent data centers, cryptocurrency miners, and hardware networks—such as Filecoin and Render—remain underutilized. This untapped potential presents an opportunity to maximize existing resources while providing a scalable solution to the anticipated compute power shortage, which is projected to be two to three times greater than the current global capacity.
The underutilization of these resources can lead to significant inefficiencies in the market, as many data centers operate at low utilization rates, resulting in bottlenecks and escalating costs. For instance, GPU hardware rental prices, often averaging around $80 per day per card, restrict access to vital computational resources for numerous AI and machine learning projects. Consequently, this financial barrier prevents many researchers and companies from fully realizing their innovative potential. By leveraging the capabilities of underutilized data centers and hardware networks, a more efficient and accessible computing ecosystem can be created. This approach alleviates the pressure on centralized providers and democratizes access to high-performance computing. As a result, a broader range of organizations can engage in AI and machine learning initiatives, fostering innovation and driving advancements across various industries.
Solution – io.net is dedicated to addressing the challenge of underutilized GPU capacity. By aggregating these dormant GPUs, io.net establishes a decentralized network that delivers computing power to users at significantly lower costs than traditional cloud services, such as AWS. This innovative approach not only maximizes the utilization of existing resources but also offers a scalable solution to the anticipated shortage of computing power, which is projected to be two to three times greater than the current global capacity.The decentralized GPU clusters provided by io.net present a cost-effective alternative, reducing expenses by up to 90% compared to traditional providers. This democratization of access to high-performance computing enables a broader range of researchers and organizations to engage in AI-driven innovations, facilitating breakthroughs that might otherwise be financially prohibitive.
Furthermore, io.net addresses the inefficiencies prevalent in data center utilization. Many data centers operate at low utilization rates, which leads to bottlenecks and drives up costs. By integrating these underutilized resources into its decentralized network, io.net enhances its efficiency and availability for AI and machine learning workloads. This reduces operational costs and improves the overall performance and reliability of computational tasks.The io.net platform aggregates GPUs from various sources, including independent data centers, cryptocurrency miners, and other hardware networks, forming a Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Network (DePIN). This network offers substantial on-demand computing power that is accessible, customizable, cost-efficient, and user-friendly.
Additionally, the io.net system empowers teams to scale workloads across the GPU network with minimal adjustments. It effectively manages orchestration, scheduling, fault tolerance, and scaling, supporting a variety of tasks such as preprocessing, distributed training, hyperparameter tuning, reinforcement learning, and model serving, all with a specific focus on AI and machine learning applications. Through these advancements, io.net is positioning itself as a leader in the next generation of cloud computing solutions.
Market Analysis
The global artificial intelligence (AI) market was valued at approximately USD 196.63 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 36.6% from 2024 to 2030. This growth is primarily fueled by ongoing research and innovation from major technology companies, driving the adoption of advanced AI technologies across various industries. In 2023, funding for AI-related Web3 projects surged to USD 298 million, doubling the USD 148.5 million raised between 2016 and 2022. AI-related tokens have also shown strong performance, with the top five AI cryptocurrencies by market capitalization significantly outperforming Bitcoin (BTC) and Ethereum (ETH), with gains ranging from 200% to 650% throughout the year. The convergence of AI and cryptocurrency has led to emerging trends and practical applications, pointing to rapid AI adoption. This trajectory signals a future increasingly shaped by AI technologies, with continued growth and innovation ahead.
Competitors
io.net faces no direct competition in the specific area of GPU clustering, where it aggregates GPU supply from underutilized sources to create a decentralized network offering nearly unlimited computing power for machine learning (ML) startups. This unique approach differentiates io.net from others in the market.
However, other companies provide GPU access for users, offering compute resources through traditional centralized platforms. They do not leverage the decentralized aggregation model that io.net uses to optimize GPU availability and cost efficiency.
- Render Network – is a decentralized GPU compute network built on Solana that connects users in need of GPU services, such as rendering and machine learning, with idle GPU owners. Through this peer-to-peer marketplace, GPU owners can monetize their unused computing power while offering creators and businesses more affordable and scalable access to GPU resources.
- Aethir- is a decentralized rendering network designed to enhance content delivery in the Metaverse. By building scalable, decentralized cloud infrastructure, Aethir allows gaming and AI companies to deliver their products directly to consumers, overcoming market fragmentation and ensuring global accessibility.
- Exabits – a decentralized infrastructure supporting AI and computationally intensive applications. It promotes an equitable and accessible AI ecosystem by enabling users to contribute GPU services, train AI models, and store data without relying on a central authority. By utilizing Web3 identities, Exabits creates a user-friendly environment for AI communities. Exabits is also a high-performance GPU supplier, providing io.net with cutting-edge GPUs, including models such as the H100s, A100s, A6000s, 4090s, and T4s.
Uniqueness
The rise of AI has significantly increased the demand for GPU computing power, resulting in a widespread shortage of GPUs in the public cloud. This has led to challenges such as long wait times, limited availability, and high costs. io.net addresses these issues by aggregating underutilized GPUs from sources like independent data centers, idle crypto mining farms, and individual consumers, offering compute power at up to 90% less than traditional cloud providers. Training AI models on a single device often leads to bottlenecks due to CPU/GPU memory limitations and sequential processing. To overcome this, io.net leverages distributed computing libraries to orchestrate and batch-train jobs, allowing for parallel processing across multiple devices using data and model parallelism. Additionally, io.net incorporates an open-source reinforcement learning (RL) library that supports large-scale, distributed RL workloads paired with a straightforward set of APIs for production use. This approach optimizes computational efficiency, making AI model training more scalable and cost-effective.
Products
io.net offers three primary products: IO Cloud, IO Worker, and IO Explorer –
IO Cloud- is a crucial service enabling users to rent and access GPU clusters and resources seamlessly. It functions as a marketplace where individuals and organizations can acquire the computational power necessary for various AI and machine learning applications, providing affordable prices up to 90% lower per TFLOP than traditional providers. IO Cloud aims to democratize access to GPUs, ensuring that machine learning engineers and developers receive an experience comparable to that of established cloud providers.
The GPU clusters, consisting of fully meshed, self-healing GPUs, form the foundational elements of IO Cloud. With IO Cloud, users can harness a decentralized network of GPUs and CPUs capable of executing Python-based machine learning code for AI projects. The RAY natively powers the platform distributed computing framework, which OpenAI utilizes to train models like GPT-3 and GPT-4 across 300,000 servers. Designed with user-friendliness in mind, IO Cloud allows users to deploy AI tasks swiftly and efficiently. Its commitment to being better, faster, and more affordable than competitors underscores its potential to significantly disrupt the traditional GPU market.
IO Workers – IO Workers are the backbone of io.net’s decentralized GPU network, allowing individuals and companies to lend their computing power for AI and machine learning tasks. By installing IO Worker software, providers can connect to the network and start earning rewards, even when their GPUs are idle. The platform is designed for easy setup, making it accessible to many users.
To ensure the authenticity and performance of resources, io.net uses an hourly Proof-of-Work (PoW) verification process. This system confirms that GPUs are genuine and performing as expected by solving complex cryptographic puzzles. The PoW mechanism also prevents fraud, ensuring only real hardware is offered and maintaining the overall reliability and quality of the network. IO Workers optimize resource utilization and enable a secure marketplace for GPU resources, offering affordable, verified computational power. This ensures fair pricing and transparent resource allocation for providers and users, making io.net a more efficient and accessible solution for high-performance computing needs.
IO Explorer – IO Explorer provides users with a comprehensive overview of the network’s metrics and data, enhancing transparency and control. It offers detailed insights into the global distribution and availability of GPUs, enabling users to select the most optimal resources based on proximity to improve performance and reduce costs. The platform also presents critical statistics on GPU clusters, compute hours, and network earnings, helping users make informed decisions. By presenting data in a clear and accessible format, IO Explorer reinforces the project’s commitment to transparency, efficiency, and user empowerment.
Traction
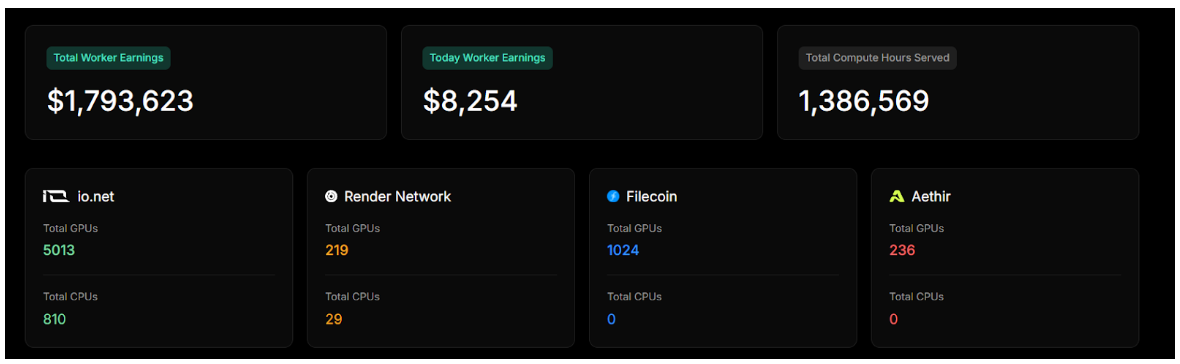
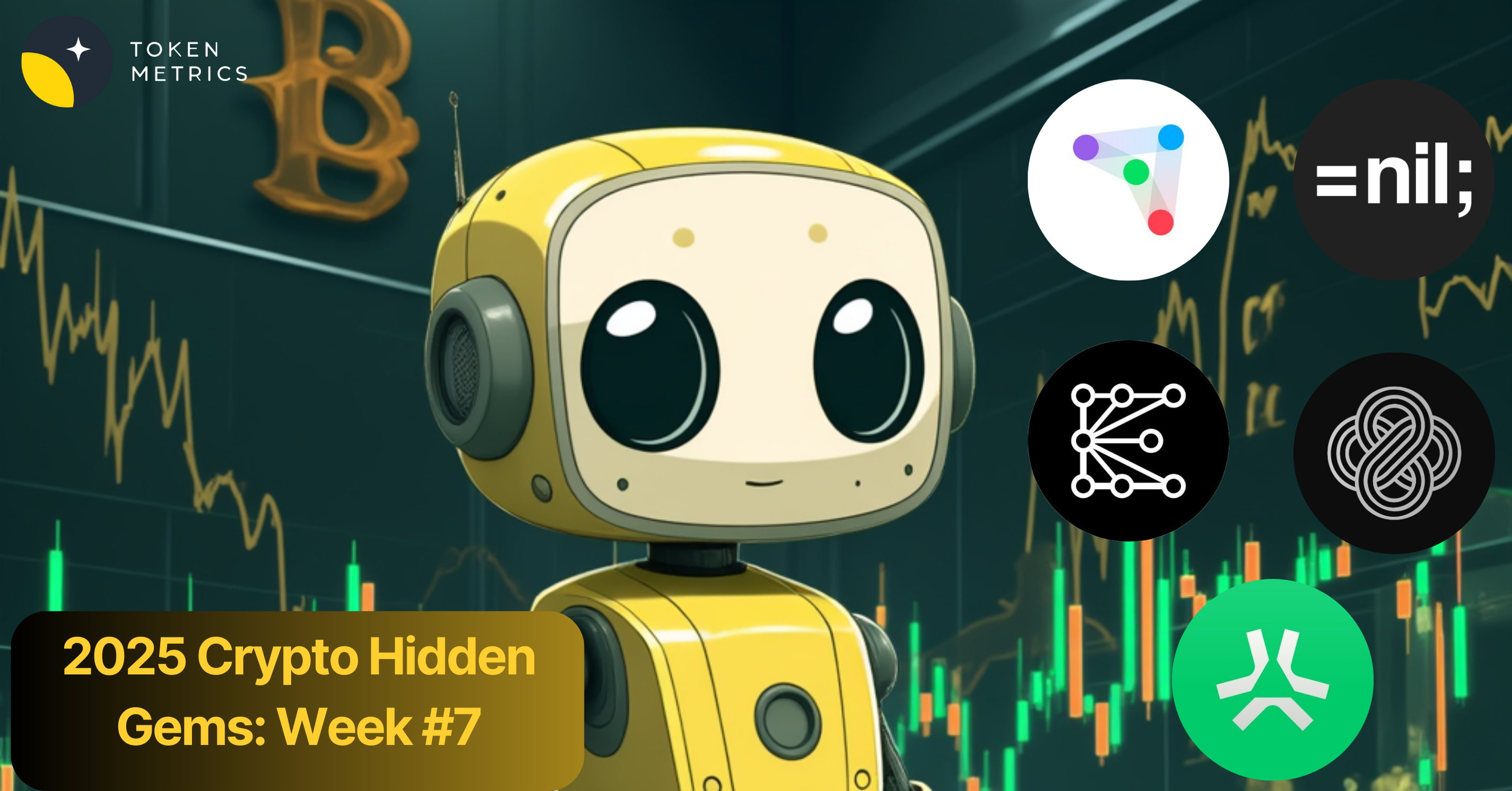
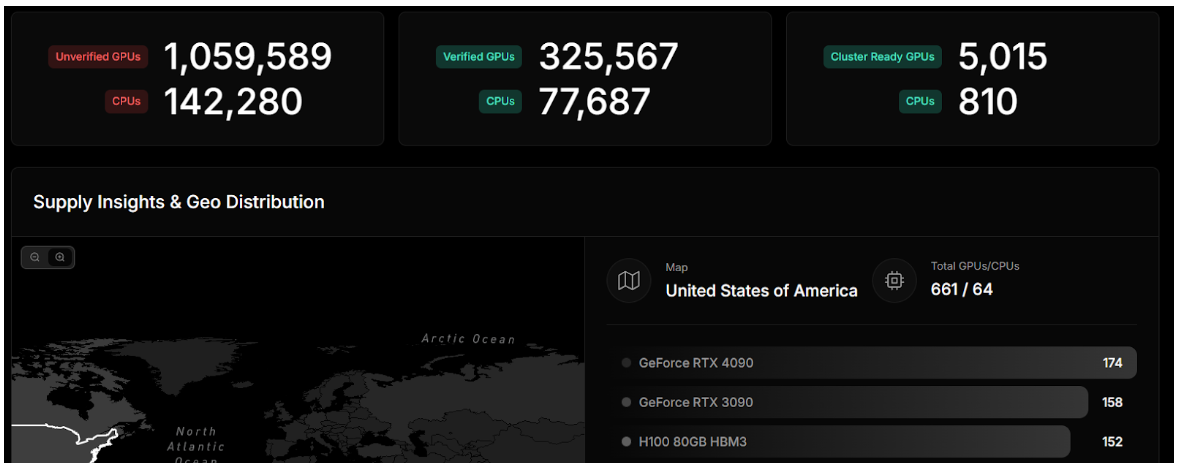
io.net has achieved significant traction within the industry, showcasing its potential as a leader in decentralized GPU computing. According to the dashboard on its website, the platform has accumulated an impressive amount of computing power, with over 1,386,323 hours of computing time served and more than 26,000 clusters created. This robust infrastructure enables users to access the necessary resources for demanding AI and machine learning applications. The network boasts over 325,000 verified GPUs, contributing to a high total inference count of 427,000, highlighting the platform’s efficiency and capability to handle extensive workloads. Additionally, io.net has established strategic partnerships with GPU providers such as Aethir, Filecoin, and Render, further enhancing its platform offerings and expanding its reach within the market.
With a fully diluted valuation (FDV) of $1.6B iio.net reflects strong acceptance and adoption in the competitive landscape of cloud computing. This valuation indicates investors’ trust in the project’s innovative approach and future potential. Furthermore, io.net benefits from a robust and engaged community, which is crucial to its growth and development. The community’s support fosters collaboration and knowledge sharing, contributing to the platform’s ongoing enhancements and establishing best practices in decentralized computing. As the demand for GPU resources continues to rise, io.net is well-positioned to capitalize on emerging opportunities, solidifying its status as a critical player in the evolving landscape of artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies.
Token

The $IO token is the native currency of io.net, governed by three key principles: a fixed maximum supply of 800 million $IO tokens, hourly rewards for suppliers and their stakers, and a burn mechanism for $IO. Known as O Coin within the IOG Network, $IO creates economic incentives for three primary groups: GPU Renters, GPU Owners, and IO Coin Holders.
GPU Renters include machine learning engineers and individual consumers seeking GPU computing power for applications such as Unreal Engine 5. GPU Owners consist of independent data centers, crypto mining farms, and professional miners aiming to monetize their underutilized GPU resources. IO Coin Holders contribute to the network’s security and growth, and may overlap with the other two roles.
In the IO Ecosystem, payments are conducted in $IO, although users can pay in fiat, USDC, or other supported tokens. While a 2% facilitation fee applies to payments made in USDC, those made in $IO incur no fees. Suppliers can also choose to receive payments in $IO, further promoting its use. The integrity of the network relies on the $IO token, requiring a minimum amount of $IO collateral to be staked for nodes to receive idle rewards. Additionally, IO Coin Holders can stake further collateral to earn rewards, enhancing the network’s overall security.
Investors

Team
Ahmad Shadid is the Founder and former CEO of io.net. His career began in the financial sector, working in mergers and acquisitions at Cordoba Partners before transitioning to roles in technology and finance. At ArabFolio Capital, he focused on crypto investments, and at WhalesTrader, he served as a quant systems engineer. Shadid gained notable recognition in 2015, winning a Gold Medal in Geneva for developing an algorithm that significantly improved real-time rendering performance for video games. After io.net, he founded the O Foundation (O.BOT) in 2024, the world’s first open-source, community-owned Super AI. Shadid left io.net before the token launch in June.
Tory Green is the current CEO of io.net. He studied economics at Stanford University in 2002 after attending the United States Military Academy at West Point. Additionally, he completed various coding boot camps in full-stack development, data science, and digital marketing. Green has held several leadership roles, including COO at Hum Capital and Director of Business Development and Strategy at Fox Mobile Group. His professional experience also includes analyst positions at Merrill Lynch and The Walt Disney Company. He later spent nine years as Principal and then Partner/COO at Tiller Partners. Green is also the Head of Global Circle at Operators Guild.
Gaurav Sharma is the CTO of io.net. He earned a Bachelor of Engineering from the Army Institute of Technology in 2007. Sharma’s career includes roles as a software engineer at Calsoft, Hewlett-Packard, and Agoda, senior developer at Amazon, and architect at eBay. Before joining io.net, he led engineering teams at Binance for two years.
Conclusion
Developers working on machine learning (ML), AI models, and other advanced computing protocols stand to gain significantly from readily accessible computing resources. This is the core vision of io.net and similar projects in the decentralized computing sector. By leveraging blockchain technology, io.net simplifies access to computational power for developers while streamlining management for providers. It enables efficient use of global computing resources by transforming idle GPUs into revenue-generating assets. Even at its early stages, io.net has already seen adoption from several projects, and as it continues to evolve, broader adoption of its decentralized approach to computing power is likely. Backed by strong investors, io.net has gained considerable traction in the market.
| Fundamental Analysis | |||||
| Assessment | |||||
| Problem | Significant, long-term problem | 3 | |||
| Solution | Distinct, defensible solution | 3 | |||
| Market Size | Large market, significant growth potential | 3 | |||
| Competitors | High competition, but room for differentiation | 2 | |||
| Unique Value Proposition | Clear differentiation and value for customers | 3 | |||
| Current Traction | Solid traction, user engagement and retention growing | 3 | |||
| Unit Economics | Positive unit economics, with plans for further improvement | 3 | |||
| Tokenomics | Basic token strategy, potential for improvement | 2 | |||
| Product Roadmap | Basic roadmap, lacks detail or innovative features | 2 | |||
| Business Model | Proven business model with clear path to profitability | 3 | |||
| Go-to-Market Strategy | Solid GTM strategy, clear target market and channels | 3 | |||
| Regulatory Risks | Minimal regulatory risk, strong mitigation and adaptability | 4 | |||
| Total | 70.83% | ||||