Executive Summary

Masa is a decentralized AI network designed to reward individuals for contributing data. It empowers AI developers to create applications using global datasets that are accessible from anywhere. As a peer-to-peer protocol, Masa seeks to establish a global, decentralized, and incentivized network for fair AI. It facilitates the equitable, open, and permissionless contribution of AI training data and computational resources, ensuring that participants are compensated according to their contributions. This paper outlines Masa’s approach to democratizing access to fair AI, detailing the network’s architecture, staking mechanisms, and reward structures that underpin this global decentralized AI network.
About the Project

Vision – Masa aims to establish itself as the world’s largest decentralized personal data network, shifting data control back to users. The platform empowers individuals to own, share, and monetize their data, redefining how data is managed and utilized in the digital age.
Problem – The current landscape of AI development is heavily influenced by a small number of centralized entities that exert significant control over access to large language models (LLMs) and compute resources. This concentration of power has resulted in several critical challenges. One of the foremost issues is that LLMs often fail to correctly attribute to the original data sources, leading to concerns over intellectual property and legal risks for companies relying on these models. Moreover, the commoditization of general-purpose LLMs has shifted the focus toward specialized AI applications, which are expected to hold the most value in the future. However, creating these specialized models requires access to niche, high-quality training data, which is typically scarce and challenging.
Additionally, the leading providers of compute and inference services often charge prohibitive prices. They can arbitrarily deny service, creating barriers to entry for smaller developers and stifling innovation within the industry. This centralization not only limits access but also poses a significant threat to the democratization of AI, where the innovation potential is constrained by a few gatekeepers.
Solution – Masa has firmly established itself as the leading marketplace for data and computing, seamlessly bridging the gap between contributors and developers within an open, permissionless environment. The platform is designed to incentivize individuals to contribute specialized data sets and offer computing resources, creating a robust, decentralized ecosystem that drives innovation in AI. Masa pioneers Fair AI by ensuring transparent attribution of contributions and rewarding participants whenever their data is utilized in applications. This addresses the critical issue of licensing risks for developers and companies and promotes ethical AI practices by giving credit where it is due. Moreover, Masa enables the contribution of specialized data for training AI models and provides access to powerful open-source LLMs, empowering developers to create highly specialized and valuable AI applications. Masa democratizes access to essential AI training data and compute resources through its open marketplace, allowing contributors to earn rewards while equipping developers with the necessary tools to drive the next wave of AI innovation. By breaking down barriers to access and fostering a fair and transparent ecosystem, Masa is setting a new standard in the AI industry, where innovation is driven by collaboration and equitable reward.
Components of Masa AI
- Decentralized AI Data Infrastructure: Masa has established a decentralized network where individuals can earn rewards by contributing data and computational resources through worker nodes. These nodes are responsible for scraping, structuring, transforming, annotating, and vectorizing various data sources. This global, permissionless system provides AI developers access to diverse datasets worldwide.
- Fair AI Attribution and Rewards: Masa is leading the charge in promoting Fair AI by ensuring transparent attribution and compensation based on the utility and value of the data contributed to the network, enabling its use in AI applications.
- Specialized Data Contributions: Masa supports the contribution, aggregation, and transformation of specialized datasets crucial for AI model training. Examples include Twitter data, Discord conversational data, and diarized podcast data.
- Open-Source LLMs: Masa offers access to fine-tuned, open-source large language models (LLMs) provisioned by network participants who operate LLM worker nodes. This infrastructure empowers developers to build specialized AI applications within a decentralized ecosystem.
- Open Network: Masa’s permissionless network democratizes access to AI training data and computational resources. Contributors are rewarded for their data and compute contributions, while developers gain the necessary resources for innovation.
How does it work?
- Worker Nodes (Users): Users operate worker nodes and stake MASA tokens to earn passive rewards. They fulfill data requests by retrieving real-time data or scraping static datasets permanently stored on the network.
- Validators: Validators are responsible for securing the Masa Network by running a Masa validator node and staking MASA tokens. They validate transactions, data contributions, and AI outputs, participate in consensus to maintain network integrity and assess the performance of worker nodes for reward distribution. Validators compete for limited slots based on performance metrics and earn rewards for ensuring network security and data quality.
- Developers (Oracle Nodes): Developers utilize the network’s diverse data and Large Language Model (LLM) services to build AI applications. They stake MASA tokens and pay dynamic fees (gas) in MASA to submit requests to the network. These requests can access real-time and static data from sources like Twitter, Discord, podcasts, and web scraping, including raw, structured, annotated, and vectorized datasets. Access is provided either by running a node or through Masa’s API.
Market Analysis
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is poised to be the defining technology of our generation, with projections indicating it could contribute an astounding $15.7 trillion to the global economy by 2030 (PwC). This anticipated growth highlights the transformative impact AI will have on the world. However, we stand at a critical crossroads as AI technology rapidly advances.
The current AI landscape is predominantly controlled by a few tech giants, including Google, OpenAI, Microsoft, Meta, and Nvidia. These “Big AI” companies monopolize the financial gains and maintain a stronghold on the economic returns from AI development. While the AI boom promises significant global economic growth, there is a growing concern that without a fundamental shift in how these benefits are distributed, history may repeat itself.
In recent years, Big Tech has accumulated trillions in value, often at the expense of people’s data privacy. A similar pattern threatens to emerge in the AI sector, potentially at an even faster pace. This concentration of power and resources within a few corporations raises serious questions about fairness, access, and the democratization of AI technology.The concept of Fair AI, driven by decentralized networks, presents a compelling alternative. As the core components of AI—compute, models, and data—should not be monopolized by centralized entities, there is a clear demand for decentralized solutions.
USP – The Masa project aims to address these challenges by achieving goals essential to developing the data and AI industries. Masa empowers individuals to have complete control over their data, allowing them to choose what to share while safeguarding their privacy. The blockchain-based storage system further ensures the security of stored data. Additionally, users can monetize access to their data, becoming primary beneficiaries of its use. These advantages starkly contrast to the traditional data collection, storage, and usage methods on Web 2.0 platforms. Another key objective of the Masa project is to provide a secure and efficient decentralized infrastructure for running Large Language Model (LLM) algorithms.
Competitors – As AI advances, blockchain technology is emerging as a powerful solution to some of the most pressing challenges in the field, particularly those related to data management and the centralization of AI models. Blockchain’s decentralized nature offers the potential to overcome many of the limitations of Large Language Models (LLMs).
Several key players, such as Bittensor, Akash Network, and io.net, are working towards providing decentralized GPU resources and LLMs, contributing to a more equitable AI ecosystem. Among these innovators is the Masa Network (MASA), an AI-focused crypto platform that introduces a new paradigm by empowering individuals to control and monetize their data. Masa’s platform also plays a significant role in the AI revolution by decentralizing the storage of both user data and the LLMs that utilize it, ensuring a more secure and democratized approach to AI development. Another project that works on monetizing data is Layer AI, but it focuses on on-chain data, whereas Masa is focusing on personal data as well.
Token
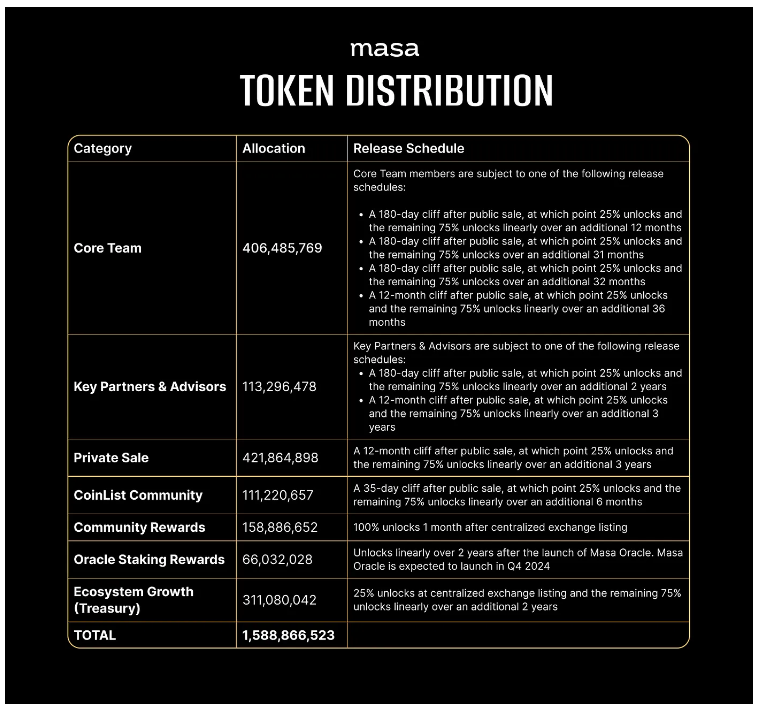
$MASA is the native utility and governance token that powers the Masa Network. It serves as a crucial component in driving the network’s use cases and enhancing its overall functionality.
- Incentivizing Data Supply: The Masa Network rewards users with $MASA tokens for contributing their personal data. Users earn passive rewards in $MASA whenever their data is utilized by businesses and developers.
- Paying for Data Use: Businesses and developers must pay fees to access and utilize the data, products, and services available on the Masa Network. These fees can be paid in $MASA tokens, stablecoins, or other blockchain-native tokens. All non-MASA-denominated fees are converted to $MASA tokens, with a portion of these tokens being burned to manage supply.
- Managing Personal Data: Users pay $MASA gas fees on the Masa Avalanche Subnet to mint and manage their zkSBT (Zero-Knowledge Soulbound Token), an encrypted personal data locker. A portion of these gas fees is burned to maintain the token’s value.
- Rewarding Node Operators: Masa Oracle node operators must stake $MASA tokens to operate zk-oracle nodes on the network. In return, they receive staking rewards for the first two years of network operation, with the staked tokens locked for a vesting period.
- Governing the Network: $MASA token holders can participate in the network’s governance by voting on proposals related to technical upgrades, fee structures, and other critical decisions. This governance model ensures that MASA holders have a say in the network’s future direction.
Where can you buy the token?
$MASA token can be bought through exchanges like Gate.io, Bybit, and BingX.
Traction
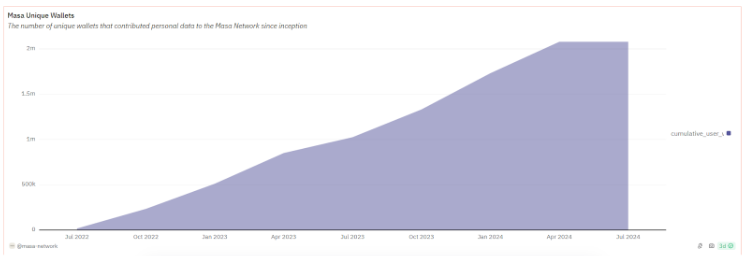
The Masa Network has quickly achieved significant milestones, demonstrating its growing influence and adoption within the blockchain and AI communities. With over 2 million unique wallets actively contributing proprietary data points, the network’s reach continues to expand rapidly. Their Dune analytics dashboard reveals that more than 10 million MASA tokens have been staked, indicating strong community engagement and confidence in the platform. The ecosystem surrounding Masa Network has also seen substantial growth. With over 70 ecosystem partners, including key industry players, the network has become a significant force in the decentralized space. Supported by leading blockchain networks such as Ethereum, Avalanche, and Scroll, Masa Network’s integration across various platforms enhances its interoperability and accessibility.
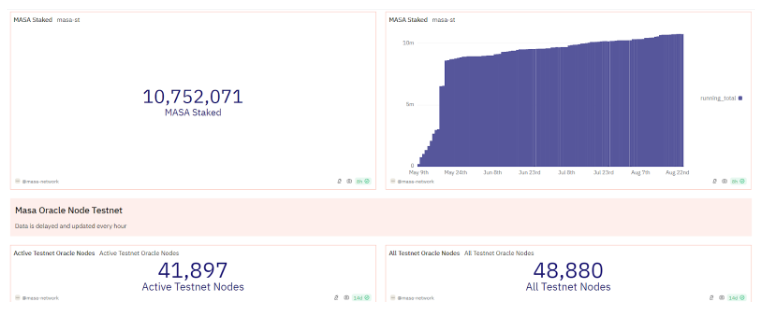
Participation in the Masa testnet has been impressive, with over 40,000 nodes actively contributing to the network’s development and stability. This level of involvement reflects the community’s high interest and commitment to advancing the Masa Network’s capabilities. Masa’s strong community presence is evident on social media, with over 200,000 followers on X and over 135,000 members on its Discord channel. This robust and growing community is a testament to the network’s appeal and the trust it has garnered among users. These metrics underscore the increasing demand for Masa AI and highlight the network’s potential for sustained growth and long-term success. As Masa continues to evolve, it is poised to play a pivotal role in the future of decentralized AI and blockchain technology, driving innovation and offering new opportunities for users and developers alike.
Team
Brendan Playford, the co-founder of Masa AI, brings extensive experience in the startup ecosystem to the venture. Calanthia Mei, the other co-founder, has a background as a senior executive at a Silicon Valley unicorn startup and has been a venture capitalist with successful exits. Before embarking on her entrepreneurial journey, she also gained experience in investment banking with HSBC. The Masa team brings extensive technical expertise, having previously worked with prominent organizations such as Coinbase, Polygon, and PayPal.
Investors

Masa AI has successfully secured $17.1 million across multiple funding rounds. In March, the company conducted a CoinList sale, raising $8 million at a valuation of $125 million. Before this, Masa AI attracted investment from a range of venture capital firms, including Avalanche Blizzard Fund, Digital Currency Group, GoldenTree Asset Management, GCR, Flori Ventures, Intersect VC, Unshackled Ventures, Alves Ventures, Peer VC, Decentranet, and LateralCapital. This diverse group of investors highlights the strong support and confidence in Masa AI’s vision and potential.
Conclusion
The Masa platform is designed to place data ownership directly in the hands of users, enabling them to manage access to their data and benefit financially from its use. As concerns about online privacy and the intrusive nature of Web 2.0 advertising continue to grow, Masa’s innovative data management approach is poised to attract a broad user base. Beyond empowering individuals to control and monetize their data, Masa is pivotal in advancing AI technologies. The platform’s decentralized data and model storage approach addresses many technical limitations associated with Large Language Models (LLMs) and other AI algorithms. This positions Masa as a network of significant merit and potential, with the key to its success lying in gaining wider recognition and user adoption.
Masa is committed to enabling individuals to contribute to and benefit from the value created by AI. By ensuring fair compensation for data contributors and providing affordable resources for developers, Masa promotes a community-driven approach to AI. This approach aims to distribute the benefits of transformative technology more equitably, fostering a more inclusive and innovative ecosystem.
| Fundamental Analysis | |||||
| Assessment | |||||
| Problem | Significant, long-term problem | 3 | |||
| Solution | Distinct, defensible solution | 3 | |||
| Market Size | Large market, significant growth potential | 3 | |||
| Competitors | High competition, but room for differentiation | 2 | |||
| Unique Value Proposition | Some differentiation, but overlap with existing solutions | 2 | |||
| Current Traction | Solid traction, user engagement and retention growing | 3 | |||
| Unit Economics | Positive unit economics, with plans for further improvement | 3 | |||
| Tokenomics | Basic token strategy, potential for improvement | 2 | |||
| Product Roadmap | Basic roadmap, lacks detail or innovative features | 2 | |||
| Business Model | Proven business model with clear path to profitability | 3 | |||
| Go-to-Market Strategy | Solid GTM strategy, clear target market and channels | 3 | |||
| Regulatory Risks | Minimal regulatory risk, strong mitigation and adaptability | 4 | |||
| Total | 68.75% | ||||