Executive Summary
Massa stands out as the pioneering layer 1 blockchain, addressing the trilemma of scalability, decentralization, and security, all without any compromises. With a capacity exceeding 10,000 transactions per second, supported by numerous nodes, our parallel block architecture and innovative Autonomous Smart Contracts (ASCs) define new benchmarks in DeFi and web3.
About the Project
Massa’s platform’s innovative parallel block architecture enables the simultaneous production of blocks across multiple threads, achieving remarkable scalability. This approach enhances the throughput of the blockchain network, accommodating a higher volume of transactions and improving overall efficiency. Furthermore, their implementation of transaction sharding plays a crucial role in enhancing the security and integrity of the blockchain. Transaction sharding ensures the reliability of transactions processed on their platform by eliminating duplicate transactions and mitigating risks such as double spending across parallel blocks. This advanced feature reinforces the trustworthiness of the blockchain, making it a robust solution for various decentralized applications and use cases.
Features-
- Scalability and Performance – One of Massa’s key features is its scalability and performance. It achieves high transaction speeds through its parallel block architecture, which allows for creating blocks in similar threads. This multithreaded block graph structure ensures scalability while organizing blocks into a complex spatio-temporal structure, further enhancing block creation performance.
- Consensus Mechanism – The blockchain’s consensus mechanism is novel and based on Proof-of-Stake, which not only enhances security and decentralization but also addresses scalability concerns.
- Autonomous Smart Contracts (ASCs) – Massa introduces Autonomous Smart Contracts (ASCs), which can autonomously execute various operations based on configured events, such as price changes. These ASCs eliminate the need for external centralized bots, revolutionizing DeFi by enabling truly autonomous operations.
- Smart Contract Language – Smart contracts in Massa are written in TypeScript, which compiles to WebAssembly bytecode (wasm). This choice of programming language makes smart contract development accessible to a wide range of developers familiar with TypeScript.
- On-Chain Web Hosting – Massa aims to host entire decentralized applications (dApps) on its blockchain, reducing reliance on centralized services. Users can browse and interact with dApps directly on the blockchain without centralized intermediaries, thereby enhancing security.
- Massa Station – Massa Station is the gateway to the Massa Blockchain, providing a desktop application that offers an intuitive way to interact with the blockchain through a web browser.
Market Analysis
Since its inception, blockchain technology has experienced exponential growth, currently reaching a valuation of $1.6 trillion, with optimistic forecasts predicting continued expansion. While prominent Layer 1 and Layer 2 solutions like Ethereum, Arbitrium, and Polygon hold significant market positions, they often need to address the blockchain trilemma, particularly in terms of decentralization. In contrast, Massa represents a new generation of Layer 1 public blockchains designed to be inclusive and decentralized. Massa tackles the traditional blockchain trilemma through technological innovation, emphasizing accessibility and decentralization by lowering the barrier to entry for running a node. Community members can become validators on the Massa network with just a few tokens, encouraging greater decentralization and mass adoption. Massa has introduced several technological innovations to support decentralization. This includes autonomous smart contracts with built-in update mechanisms and on-chain web page storage to bypass traditional centralized web servers. These innovations further enhance the platform’s focus on decentralization and user empowerment.
Traction
Massa launched its mainnet on January 15 of this year. Within two weeks of its launch, the network welcomed over 1,800 stakers and processed over 80,000 operations. Notably, these operations included deploying new autonomous smart contracts, highlighting the platform’s advanced capabilities and rapid adoption.
Token
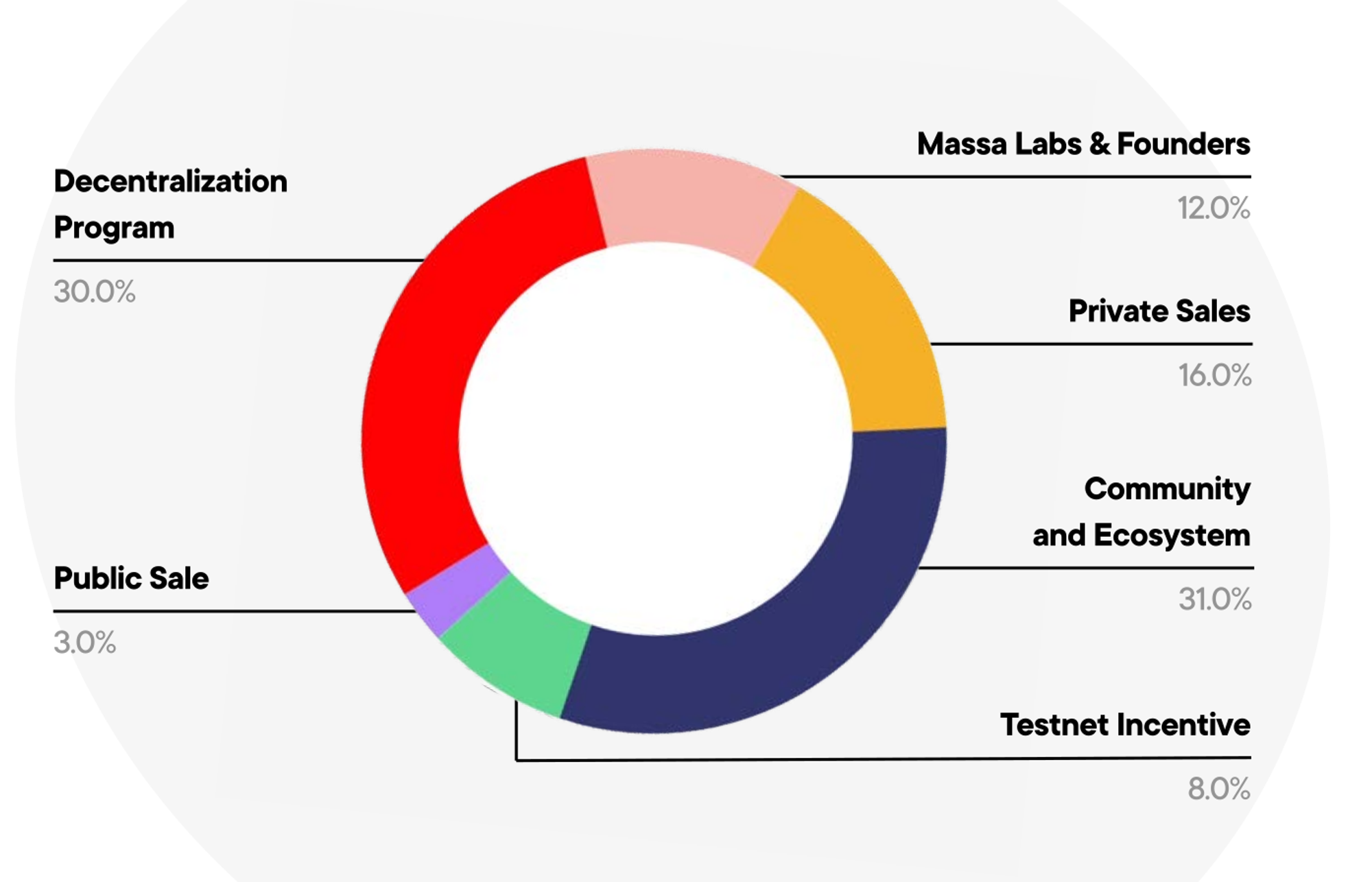
Massa has implemented a unique tokenomics model that prioritizes fairness and decentralization. Massa is steadfast in its commitment to upholding high standards of decentralization, aiming to achieve a Nakamoto coefficient of over 1,000. This goal is set to ensure that control and decision-making authority are dispersed widely throughout the community. The total initial token supply of Massa is 1 billion tokens. The Massa token serves to access the platform and participate in staking activities.
Investors

Massa Team

Conclusion
Massa is a public blockchain that prioritizes scalability, efficiency, and security. One of its key innovations is implementing a novel Proof-of-Stake consensus mechanism, which significantly enhances throughput by parallelizing block creation, enabling the processing of up to 10,000 transactions per second. This approach addresses a longstanding challenge in the cryptocurrency space: creating a scalable, decentralized blockchain. The platform’s unique features and alignment with market demands suggest a strong potential for growth and adoption in the evolving blockchain landscape.
Token Metrics Ventures is excited to invest and happy to introduce the team to any LPs interested in learning more about Massa.
| Fundamental Analysis | |||||
| Assessment | |||||
| Problem | Moderate, somewhat persistent problem | 2 | |||
| Solution | Some uniqueness, moderate defensibility | 2 | |||
| Market Size | Large market, significant growth potential | 3 | |||
| Competitors | High competition, but room for differentiation | 2 | |||
| Unique Value Proposition | Clear differentiation and value for customers | 3 | |||
| Current Traction | Early traction, user engagement starting to grow | 2 | |||
| Unit Economics | Strongly positive unit economics, scalable with growth | 4 | |||
| Tokenomics | Solid token strategy, aligns with user incentives | 3 | |||
| Product Roadmap | Unclear or unrealistic product roadmap | 1 | |||
| Business Model | Proven business model with clear path to profitability | 3 | |||
| Go-to-Market Strategy | Basic GTM strategy, lacks detail or differentiation | 2 | |||
| Regulatory Risks | Minimal regulatory risk, strong mitigation and adaptability | 4 | |||
| Total | 64.58% | ||||