Nillion is building a decentralized internet infrastructure platform based on cryptography. The company has developed a technology called Nil Message Compute (NMC) for secure, fast, and efficient data processing. Unlike blockchains, Nillion’s network of nodes does not store full data copies or process transactions, but instead focuses on decentralized computation. It leverages privacy-enhancing technologies (PETs) like Multi-Party Computation (MPC) to protect high-value data during processing. This allows computations to be performed on masked data without decryption, significantly enhancing security. Nillion decentralizes trust in data computation, similar to how blockchains decentralize transactions. Its unique approach has the potential to transform how companies and users pursue decentralization.
About the Project
Vision – Nillion envisions a future where decentralized, private data powers the world’s biggest industries. Using its Nil Message Compute (NMC) technology, it enables fast, secure, and efficient computation without full data replication. By leveraging privacy-enhancing technologies like Multi-Party Computation (MPC), Nillion allows masked data processing, unlocking new Web3 use cases. This vision aims to make Nillion a core infrastructure layer for the next generation of decentralized applications.
Problem – The Problem Nillion Solves
Handling high-value data traditionally faces three major challenges: secure storage, secure computation, and decentralized data management. Typically, sensitive data must be encrypted during storage and decrypted for use, creating security risks and inefficiencies. Decentralizing data across nodes introduces complexities in maintaining security and computational efficiency.
Nillion’s Nil Message Compute (NMC) technology allows data to be stored and processed in a decentralized network without ever needing to decrypt it. Instead of full data copies being stored on each node, only fragments are distributed, enhancing both privacy and efficiency. By enabling computation on masked data, Nillion eliminates the need for the risky decrypt-compute-reencrypt cycle.
A good example of the Nillion application is in health – imagine a healthcare platform analyzing patient data to detect disease patterns. Traditionally, patient data would need to be decrypted, processed, and then re-encrypted, exposing it to potential breaches. With Nillion, this analysis can happen directly on masked data, ensuring privacy while enabling real-time insights — all without risking exposure of sensitive patient information.
Solution
Nillion provides a solution for secure, decentralized computation using Nil Message Compute (NMC) technology and a novel Multi-Party Computation (MPC) protocol. Unlike traditional methods that require decrypting data before processing, Nillion enables computation directly on masked data, preserving privacy and security.
Nillion’s dual-layer architecture consists of the NilChain and Petnet networks. The NilChain coordinates payments and computations, while the Petnet handles data storage and processing. Data is not fully stored on any single node but instead split into fragments distributed across nodes, enhancing privacy and efficiency.
The computation process begins with pre-processing, where input data is converted into “shares” (or masks) using Linear Secret-Sharing Schemes (LSSS). These shares are distributed to nodes, and computation is then performed locally on the masked data without revealing the original inputs. Each node computes independently in a non-interactive process, speeding up operations and reducing network overhead. The final result is aggregated from local computations, ensuring no sensitive data is ever exposed.
This approach eliminates the need for the decrypt-compute-reencrypt cycle, which is common in traditional methods, while maintaining Information-Theoretic Security (ITS). For example, a healthcare provider can analyze encrypted patient data without exposing it. The data is split, masked, processed locally on nodes, and aggregated to produce insights, all while keeping the original data private. Nillion’s secure computation model supports industries like healthcare, finance, and AI, enabling privacy-first data analysis and unlocking new Web3 applications.
Market Analysis
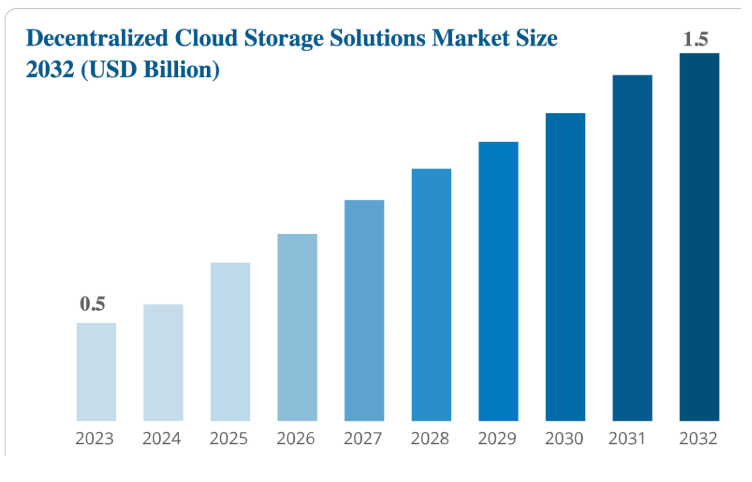
The decentralized data storage market is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for privacy, security, and compliance in data management. This market stands in contrast to traditional centralized storage solutions, which have been criticized for their vulnerabilities and privacy concerns. The global decentralized cloud storage market was valued at approximately $0.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach $1.5 billion by 2032, exhibiting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 15% during this period – Business Research. Another report from Global Market Insight estimates that the broader decentralized storage market will grow from $622.9 million in 2024 to approximately $4.5 billion by 2034, with a CAGR of 22.4% between 2025 and 2034.
Drivers of this Market Growth
- Data Privacy and Security Concerns: Increasing incidents of data breaches have heightened the need for secure storage solutions that minimize the risk of unauthorized access. Decentralized systems distribute data across multiple nodes, reducing single points of failure and enhancing security.
- Regulatory Compliance: Stricter data protection regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA are prompting organizations to adopt decentralized solutions that allow for better control over data sovereignty and compliance with local laws
Statistics from Coingecko further highlights the combined market cap of storage tokens to be $9.9bn, with projects like Filecoin, Arweave, Bittorrent and AIOZ network leading the wave.
Competitors
While there are alot of decentralized storage networks/platforms out there, Filecoin differentiates itself as one of the leaders in this segment.
Filecoin – A decentralized storage network that uses blockchain technology to create a marketplace for storage services. Filecoin allows users to pay for storage using its native cryptocurrency, FIL, and ensures data integrity through a proof-of-storage consensus mechanism.
Uniqueness Value Proposition of Nillion
Nillion utilizes its Nil Message Compute (NMC) technology to facilitate computations on masked data without the need for decryption. This unique capability allows Nillion to maintain data privacy and security during processing, making it particularly attractive for industries that handle sensitive information, such as healthcare and finance. In contrast, Filecoin operates as a decentralized storage network that incentivizes users to rent out their unused storage space in exchange for FIL tokens. Filecoin’s architecture is built on the InterPlanetary File System (IPFS), which focuses on creating a distributed storage solution where files are stored across multiple nodes. However, it requires users to decrypt data for processing, which can introduce security vulnerabilities.
While both platforms prioritize decentralization, their primary objectives differ. Nillion emphasizes privacy-preserving computation, enabling secure data processing without exposing sensitive information. Filecoin, on the other hand, aims to disrupt traditional cloud storage providers by offering a low-cost alternative for temporary data storage. This focus on affordability positions Filecoin as a competitor to established giants like Amazon Web Services and Google Cloud; however, it may struggle against these incumbents’ economies of scale.
Target Audience and Use Case
Nillion’s target audience includes enterprises, developers, and organizations that prioritize privacy, security, and decentralized data computation. Key industries include healthcare, finance, artificial intelligence (AI), and legal services. Use cases include privacy-preserving patient data analysis, secure financial risk assessments, privacy-focused AI model training, and confidential document processing.
Features
- Blind Computation on Masked Data: Nillion enables secure computation on encrypted data without decryption, preserving privacy throughout the process.
- Nil Message Compute (NMC) Technology: The platform’s use of NMC Technology allows efficient, privacy-first computation without requiring global state synchronization or transaction ordering.
- Multi-Party Computation (MPC) Protocol: Nillion supports non-linear operations on fragmented data, enabling secure and decentralized computation.
- Dual-Layer Network Architecture: Combines the NilChain (payment coordination) and Petnet (data storage and computation) for decentralized data management.
- Information-Theoretic Security (ITS): Provides protection against adversaries with unlimited computing power, ensuring maximum privacy and data security.
- Asynchronous, Non-Interactive Computation: Local computations on masked data happen independently, reducing communication overhead and improving processing speed.
- Decentralized Data Storage: On the Nillion’s Network, Data is split into shares and distributed across nodes, eliminating the need for a single point of trust or centralized storage.
- Privacy-Enhancing Technologies (PETs): Nillion Utilizes advanced PETs like MPC and LSSS to maintain privacy, making it ideal for industries with strict privacy requirements.
Traction
Nillion boast of a strong ecosystem, onboarding over 33+ blockchain network including NEAR Protocol, APTOS, and Arbitrium.
Investors
Nillion has successfully raised a total of $50 million to date, with the most recent funding round securing $25 million. This latest round was led by Hack VC and included participation from several notable venture capitalists and industry leaders, such as Distributed Global, Hashkey, Ansem, Arthur Hayes, and Meltem Demirors. Additionally, influential figures from organizations like Worldcoin, Injective, and Sei contributed to this funding effort.
Team
The team at Nillion have strong industry experience with notable sectors such as venture capital, fintech.
Alex Page – Currently leads Nillion as the CEO. Alex also functions as an Investment principal at Hedera Hashgraph. A graduate of Southern Methodist University.
Andrew Masanto – Currently a Co-founder of Nillion. Andrew was previously the founding Chief Marketing Officer at Reserve, the most used fintech in Argentina which has processed over $3.7mn in transactions. Also sits on the board of Cornerstone capital. A graduate of University of Sydney.
Nathan M– Currently the Founding Head of Growth at Nillion. 2 X founder with an exit. Nathan also has experience in partnership while working as a partnership manager at Zurich Insurance. Graduated from the University of Birmingham.
Lukas Bruel – Functions as the Head of ecosystem and AI strategy. Lukas has a strong corporate experience. Graduated from University of Cambridge.
Conclusion
Nillion is a decentralized network that enables secure computation on private data without requiring decryption. Traditional methods expose sensitive information during computation, creating privacy risks and inefficiencies. Nillion solves this by using its Nil Message Compute (NMC) technology and Multi-Party Computation (MPC) protocol to process masked data directly. This allows organizations to store, compute, and analyze high-value data securely while maintaining privacy and regulatory compliance. By decentralizing trust and enabling privacy-preserving computation, Nillion positions itself as a key infrastructure for privacy-first Web3 applications.
| Fundamental Score | |||||
| Max score | Options | Score | |||
| Problem | 10 | Significant, long-term problem | 9 | ||
| Solution | 10 | Distinct, defensible solution | 9 | ||
| Market Size | 10 | Moderate market with potential for growth | 7 | ||
| Competitors | 10 | Emerging market with few strong competitors | 8.5 | ||
| Use case | 10 | Use case with good potential | 8.5 | ||
| Current Traction | 10 | No or very limited user engagement | 4 | ||
| Unit Economics | 5 | Unit economics currently negative, no clear path to profitability | 1 | ||
| Tokenomics | 10 | Basic token strategy, potential for improvement | 7 | ||
| Product Roadmap | 5 | Basic roadmap, lacks detail or innovative features | 2 | ||
| Business Model | 10 | Business model with some potential, but improvement needed | 7 | ||
| Go-to-Market Strategy | 5 | Basic GTM strategy, lacks detail or differentiation | 2 | ||
| Community | 5 | Acive and growing community | 4 | ||
| Regulatory Risks | 5 | Minimal regulatory risk, strong mitigation and adaptability | 5 | ||
| Total Score | 70.48% | ||||