Onocoy is a decentralized network that delivers high-precision GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) data worldwide. Using blockchain, it supports a community-driven infrastructure of reference stations that enables Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) positioning, providing meter-level accuracy for industries like agriculture, construction, autonomous systems, and drone operations. By applying decentralized principles, Onocoy creates a densely distributed network of GNSS reference stations, offering high-quality, pay-per-use correction data for applications such as drones, autonomous vehicles, robotic lawnmowers, and more. Users who set up these reference stations to facilitate accurate data reporting are rewarded with the ONO token.
About the Project
Vision – Onocoy’s vision is to create a global, community-driven network that makes high-precision GNSS correction data accessible to anyone, anywhere. By empowering individuals and communities to contribute their own GNSS reference stations, Onocoy aims to democratize access to centimeter-level positioning accuracy, which is essential for a range of industries and applications.
Problem – Onocoy is tackling several issues with how high-accuracy GNSS positioning data is provided today. Right now, setting up and maintaining GNSS reference stations is costly. As a result, service providers usually focus on wealthy regions and high-paying clients, like those in specialized industries, leaving other regions and users with limited options.
For example, in a rural farming community that could benefit from precise tractor guidance systems, there might be no affordable GNSS correction services available. This limited access creates big gaps, especially as new industries like drone deliveries, autonomous vehicles, and even small robotic mowers are becoming mainstream and need high-precision GPS data. Another problem is that many providers operate independently, building duplicate reference stations in the same areas without working together. This redundancy raises costs unnecessarily, and these costs get passed on to the customer.
Additionally, service providers are often set up for specific, high-end markets, making it difficult to offer their services to everyday users or in smaller markets. Fragmented services also make it hard for global companies to get the same data quality worldwide. A company that needs GPS accuracy for self-driving cars in both Tokyo and San Francisco might struggle to find a reliable, unified service.
Finally, most providers don’t allow access to raw GNSS data from their reference stations, limiting flexibility for scientific and other specialized uses. If a research institution wanted raw GNSS data for climate research or earthquake monitoring across continents, it would be nearly impossible with current options.
Onocoy is solving these issues by creating a decentralized network of reference stations that anyone can contribute to. This community-driven approach not only reduces costs but also brings GNSS correction services to more areas, offering pay-per-use options that fit mass markets, from hobbyists to large companies.
Solution
Onocoy’s solution provides a decentralized, blockchain-based network of GNSS reference stations powered by individual and community contributions. Instead of relying on centralized providers that incur high infrastructure costs and focus on profitable markets, Onocoy allows users to set up and connect their own GNSS stations to the network. This community-driven approach builds a dense, widespread network that offers reliable GNSS correction data at a lower cost.
By connecting to the network, users enable their stations to deliver Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) correction data, providing a meter-level positioning accuracy. As a reward, users earn incentives, which encourage further participation and expand the network’s coverage. This model avoids duplication of infrastructure and keeps operational costs low, making it feasible to offer high-accuracy GNSS data in regions often neglected by traditional providers.
Through its decentralized design, Onocoy supports global, flexible, pay-per-use access to GNSS correction data, suitable for mass-market and niche applications alike. This structure benefits industries such as agriculture, construction, and autonomous vehicles, which rely on high-precision GPS. Additionally, Onocoy grants access to raw GNSS data, accommodating specialized needs like scientific research and environmental monitoring.
Market Analysis
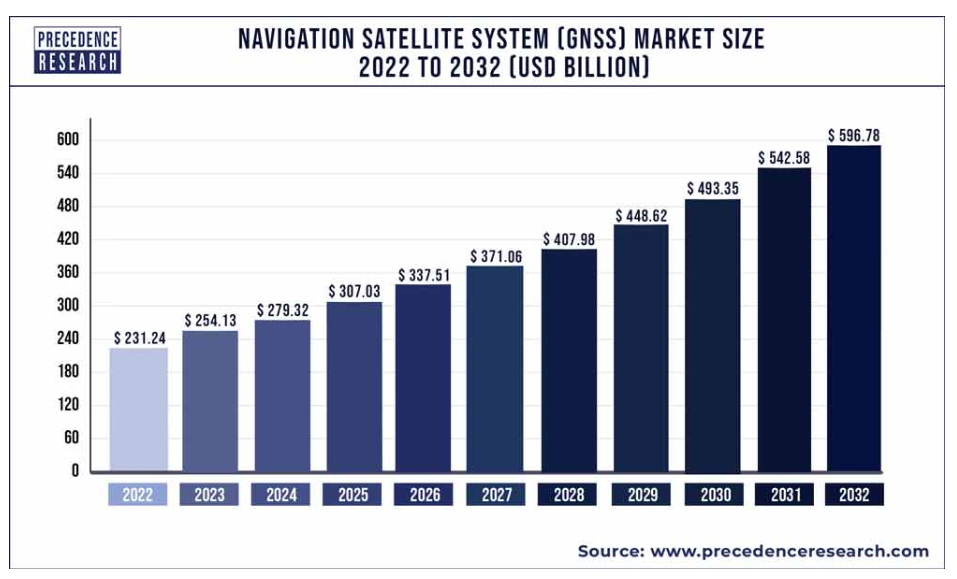
Onocoy is positioned in the growing GNSS correction data market, crucial for high-precision applications across sectors like agriculture, construction, and logistics. The global GNSS market was valued at approximately $223 billion in 2021, with a projected CAGR of 10% through 2030. The RTK segment is expected to reach $5.6 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 18.2%. The GNSS market is driven by increased demand for location-based services across industries, particularly in logistics and autonomous vehicles. Technological advancements, including the integration of 5G and IoT, enhance the accuracy and reliability of GNSS systems. Rising investments in satellite navigation programs by governments and private entities further support market growth. Established Web2 competitors like Trimble and Leica Geosystems dominate the market but focus on high-end solutions. Onocoy’s innovative approach could bring change to the market by making precision positioning more affordable and widely available.
Competitors
While most large competitors are web2 based, there are few key competitors building within the Web3 space.
Geodnet – Geodnet focuses on improving GPS accuracy and reliability through a decentralized network of Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) reference stations. GEODNET incentivizes individuals to install geodetic-grade GNSS antennas, allowing them to contribute to a global network that provides centimeter-level accuracy for various applications, including agriculture and autonomous vehicles. Geodnet rewards participants with GEOD tokens, fostering a community-driven approach to expand its coverage and reduce cost. Geod token is public and has a market cap of $42mn as at the time of this writing.
Uniqueness – While both Onocoy and GEODNET share similar products and principles for rewarding users, their approaches and priorities differ significantly. Onocoy focuses on inclusivity, particularly in rural regions globally, ensuring that high-precision GNSS data is accessible to underserved communities. The company’s business model utilizes a pay-per-use structure, allowing developers to integrate its API and pay based on their actual usage. This model promotes flexibility and cost-effectiveness for users across various sectors.
In contrast, GEODNET operates on a fixed subscription model, requiring users to pay a set monthly or yearly fee for access to its services. This approach may limit accessibility for smaller businesses or users in less affluent areas.
Features
Community-Driven Reference Network: Onocoy relies on a decentralized infrastructure of GNSS reference stations contributed by individuals and organizations worldwide. This community-powered approach helps reduce infrastructure costs, encourages widespread participation, and broadens coverage beyond high-income or urban areas.
High-Precision Positioning: Onocoy delivers Meter-level GNSS positioning accuracy using Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) correction data, which is essential for applications in fields like autonomous systems, precision agriculture, and construction. This high accuracy level supports safer and more efficient operations for positioning-dependent technology.
Global Coverage with Pay-Per-Use Access: The company offers a flexible, pay-per-use model, making high-accuracy GNSS correction data accessible to a global audience, including underserved and rural areas. Developers only pay for the data they need, making the service scalable for both small and large-scale applications across diverse regions.
Access to Raw GNSS Data: Onocoy provides access to raw station measurements, which can be valuable for specialized use cases, including scientific research, environmental monitoring, and advanced positioning solutions. T
Traction
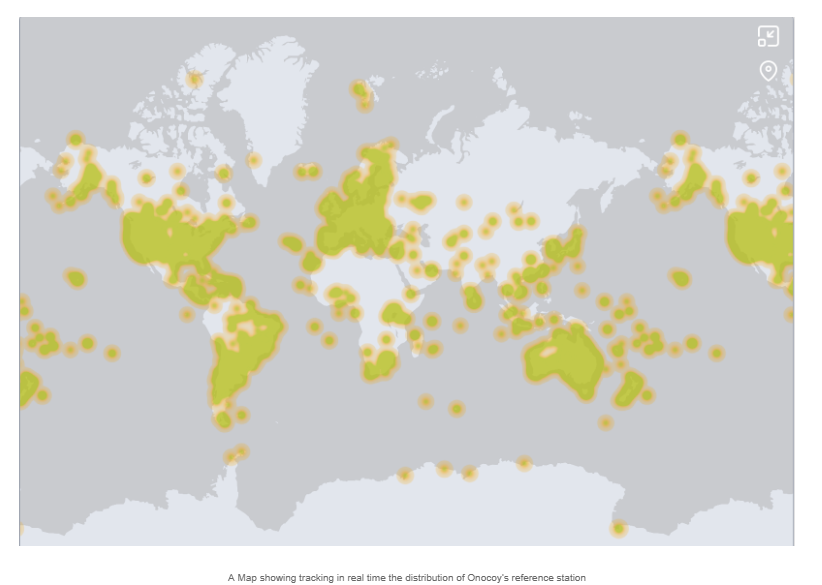
Despite being in its early stages and operating at the intersection of hardware and software, Onocoy has amassed a total of 4,210 validated reference stations, with 3,499 actively online. This indicates that over 80% of its users are active and consistently contribute to the network.
Investors
Since its inception, Onocoy has raised a total of $4.2 million from industry-based Web 2 investors as well as native Web3 investors. Its recent token round raised $940,000 from Web3-native VC Smart Island Capital, which has also invested in well-known DePIN projects such as Peaq and GEODNET. Other investors include the European Union Agency for Space Programme.
Team
The founders of Onocoy have strong industry experience relevant to GNSS, hence positioning themselves as the right team to solve this problem.
Daniel Ammann – Currently Leads Onocy as the CEO. He has a background in GNSS, functioning as the Chairman of Fixposition, a startup that combines GNSS with computer vision for autonomous systems.
Samuel Q – Samuel has a background in Data Analysis, as well as consulting. He was previously a Data analyst at KPMG. He also functioned as a technical consultant at Accenture. Web3 experience includes his role as a Research Assistant at ETH AI.
Conclusion
Onocoy is positioned to tackle the GNSS correction data industry with its decentralized, community-powered network offering global, high-precision positioning. By reducing infrastructure costs, expanding access to underserved regions, and enabling new applications through raw data access, Onocoy serves a growing market with mass-market potential. With over 80% active contributors and $4.2 million raised, including backing from investors, Onocoy is well-supported for scalable growth and innovation in the DePIN space.
| Fundamental Score | |||||
| Max score | Options | Score | |||
| Problem | 10 | Significant, long-term problem | 9 | ||
| Solution | 10 | Distinct, defensible solution | 9 | ||
| Market Size | 10 | Large market, significant growth potential | 8.5 | ||
| Competitors | 10 | High competition, but room for differentiation | 7 | ||
| Use case | 10 | Use case with good potential | 8.5 | ||
| Current Traction | 10 | Early traction, user engagement starting to grow | 6 | ||
| Unit Economics | 5 | Break-even or slightly positive unit economics | 2 | ||
| Tokenomics | 10 | Basic token strategy, potential for improvement | 7 | ||
| Product Roadmap | 5 | Unclear or unrealistic product roadmap | 1 | ||
| Business Model | 10 | Business model with some potential, but improvement needed | 7 | ||
| Go-to-Market Strategy | 5 | Basic GTM strategy, lacks detail or differentiation | 2 | ||
| Community | 5 | Acive and growing community | 4 | ||
| Regulatory Risks | 5 | Moderate regulatory risk, solid mitigation strategy | 4 | ||
| Total Score | 71.43% | ||||