
Introduction
Veda positions itself as a DeFi engine for institutional‑grade financial applications. It provides a standardized vault infrastructure—called the BoringVault—that underpins on‑chain financial products with modular, audited smart contracts and supporting developer tooling. With over $3.5B in total value secured and $100M+ actively deployed in strategies, Veda serves as a foundational primitive for pricing, accounting, and automating capital flows across multiple chains and protocols.
Innovation
Veda’s primary innovation is its approach to vault infrastructure:
Vault as a Primitive:
Instead of bespoke vault logic for each product, Veda offers a minimal, auditable core that delegates complexity to modules.Protocol‑ and Chain‑Agnostic Integration:
Supports EVM, SVM, MoveVM, and connects to various DeFi ecosystems without major re‑engineering.Compliance‑Aware Controls:
Features like address whitelists, curator roles, and permissioned deposits allow vaults to adapt to regulatory or internal constraints.Composable Vault Shares:
Veda vault shares have been integrated into lending markets such as Aave’s main market, a first for vault tokens.
Find out why 1M+ professionals read Superhuman AI daily.
AI won't take over the world. People who know how to use AI will.
Here's how to stay ahead with AI:
Sign up for Superhuman AI. The AI newsletter read by 1M+ pros.
Master AI tools, tutorials, and news in just 3 minutes a day.
Become 10X more productive using AI.
Architecture
Veda employs a modular vault architecture designed for security and extensibility:
BoringVault (Core Contract):
A minimal contract (~100 lines of core logic) holding user deposits. All operational complexity is delegated to external modules.Key Modules:
Teller: Handles deposits, minting/redeeming vault shares, and enforces lock periods or refunds.
Manager: Allocates and rebalances funds into whitelisted strategies using Merkle‑proof validation for strict access control.
Accountant: Maintains exchange rates and ensures updates are within safe bounds; can pause updates in anomalous conditions.
Oracle: Updates vault yield and asset values with on‑chain constraints like max deviation and update frequency.
Flow of Funds:
Users deposit via Teller → shares are issued based on Accountant rates → funds are allocated daily by the Curator through Manager‑approved strategies → withdrawals are routed through a separate withdrawal contract for added security.
This separation of concerns isolates risks, simplifies audits, and enables rapid deployment of new vault strategies.
Code Quality
The design emphasizes security, minimalism, and extensibility:
Minimal Core Logic:
The BoringVault’s lean codebase reduces attack surface and simplifies audits.Merkle‑Proof Strategy Control:
Ensures only authorized strategy calls are executed, adding a verifiable layer of security.Upgrade‑Friendly Modules:
Because modules (Manager, Teller, Accountant) are external, they can be updated or replaced without disrupting core vault contracts.Audited Smart Contracts:
Funds remain non‑custodial in audited contracts, and vault operations are transparent on‑chain.
The overall approach shows strong adherence to best practices in DeFi contract engineering.
Product Roadmap
While explicit future milestones are not publicly detailed, likely directions include:
Expanding Cross‑Chain Support:
Continued integration with non‑EVM environments (e.g., SVM, MoveVM).Advanced Strategy Modules:
Additional optimization logic and new DeFi integrations.Compliance Tooling:
Further development of whitelist/permission layers for institutional users.Enhanced SDK/APIs:
More features in developer tooling to enable third‑party financial product deployment.
Usability
For Institutions:
Ready‑made infrastructure to launch branded DeFi products without rebuilding core vault logic. Whitelists and permissions make compliance management straightforward.For Developers:
SDKs and APIs lower integration complexity; modular design allows rapid iteration (new vaults or strategies in ~48 hours).For End Users:
Depositing and withdrawing through Teller is straightforward, though some operational details (e.g., withdrawal periods) depend on vault configuration.
Conclusion
Veda delivers a robust vault infrastructure layer that abstracts away complexity for institutions and developers building on‑chain financial products. Its modular, minimal core architecture paired with compliance features and cross‑chain compatibility make it stand out as a DeFi primitive rather than a single‑purpose protocol.
Veda represents a mature, technically sound vault framework that underpins a growing ecosystem of institutional DeFi products. Its separation of core and modular components demonstrates best practices in smart contract design, making it a significant infrastructure component in decentralized finance.
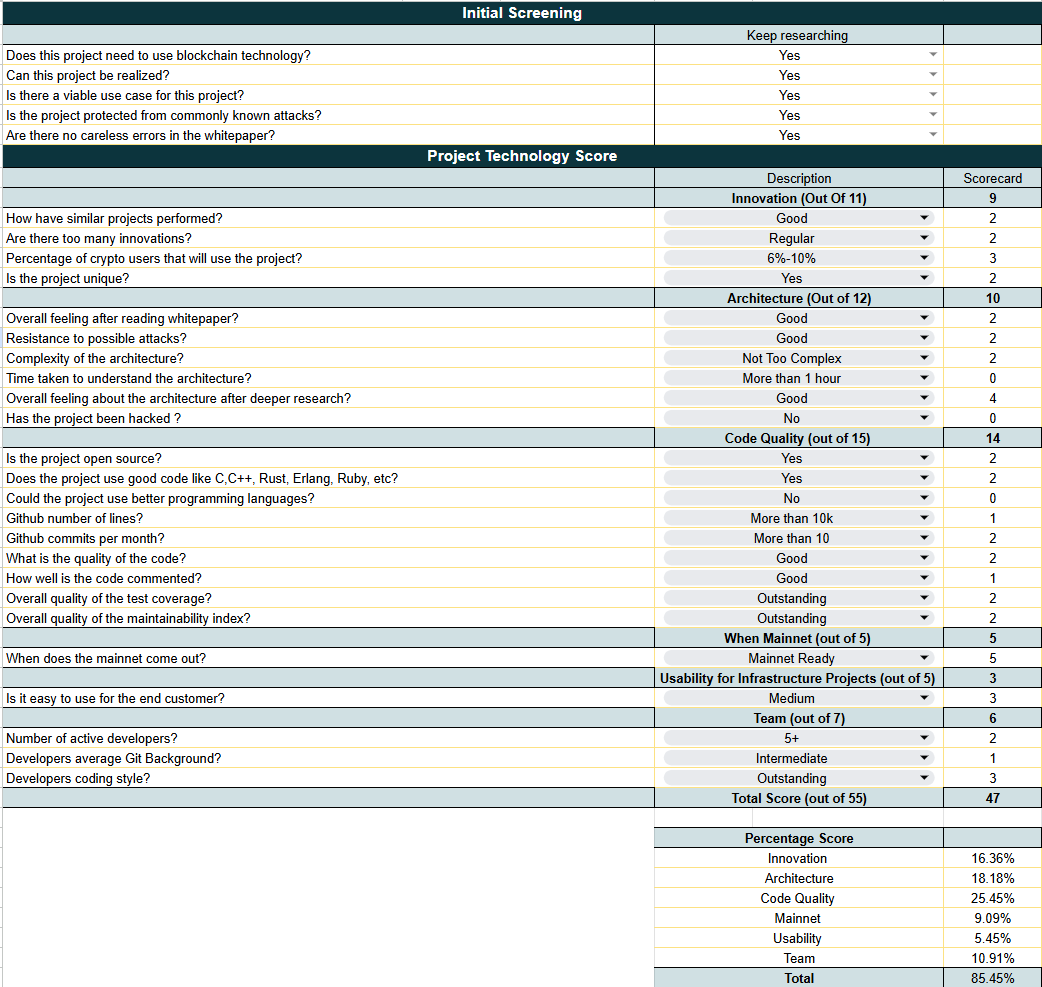
Veda Scorecard


