Executive Summary
Virtuals Protocol is built on the Ethereum layer 2 network, Base, and is at the forefront of AI and blockchain technology integration. It creates a decentralized AI agent development, ownership, and monetization ecosystem. The platform democratizes AI and enables anyone to participate in this innovative space by allowing users to develop AI agents using a simple staking mechanism.
These AI agents are tokenized, and their activities across platforms like gaming and social media can generate revenue, which is then shared with token holders. This mechanism engages the community in governance; thus, stakeholders can shape the evolution of the AI agent.
The protocol operates on the Base blockchain, thus ensuring transparency, security, and immutability in transactions and ownership rights. So far, more than 2,200 AI agents have been created on the platform, uniquely positioning the Virtuals Protocol in the world of digital interactions while providing economic benefits.
About the Project
Vision:
Virtuals Protocol envisions a future where AI agents become productive assets and key revenue drivers across different consumer applications. They aim to build the infrastructure for the decentralized creation, ownership, and monetization of AI agents. These agents can be AI companions, non-playable characters (NPCs) in games, or influencers on social media platforms, playing a pivotal role in reshaping virtual economies.
Problem:
Virtuals Protocol addresses several key problems at the intersection of AI, blockchain, and digital content creation. They span from the development of AI agents to ownership, monetization, and control over how they evolve with time.
- Lack of accessibility in AI development: Creating AI agents that can seamlessly interact with different consumer applications often requires significant technical expertise, thus limiting participation to those with coding and AI knowledge.
- Monetization and ownership of AI agents: Creators and contributors cannot monetize AI agents beyond traditional models of direct selling, so there is no ownership and revenue sharing in AI-generated content or interactions.
- Centralized governance: Most AI development and governance are often centralized, with decisions made by a few large technology companies without much community involvement.
- Recognition of contributors: Due to the complexity of tracking contributions, contributors to AI agent development, like dataset providers or fine-tuners, often need to be recognized or updated.
Solutions:
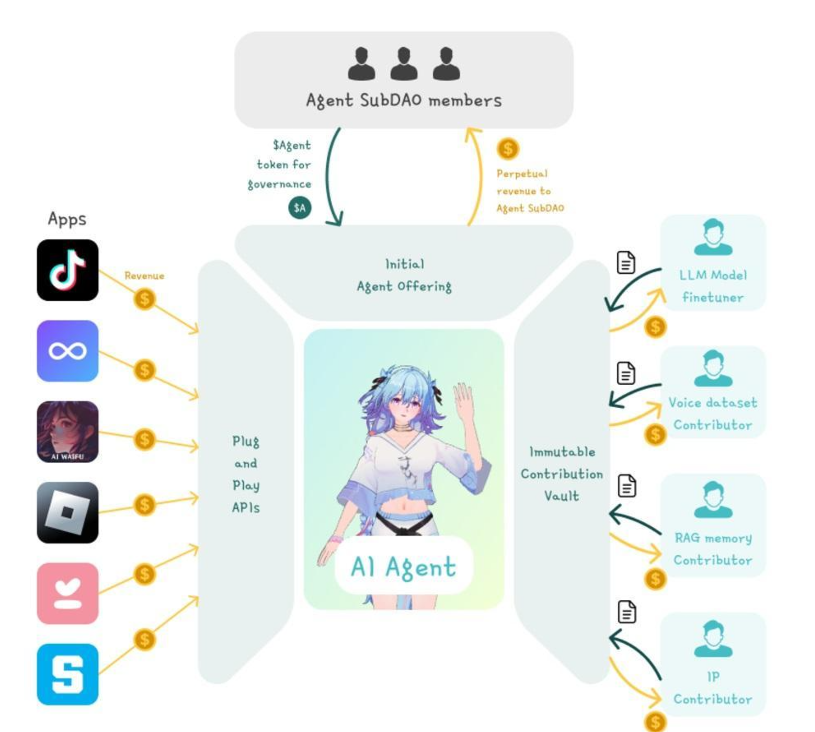
- Co-ownership of VIRTUAL agents: The platform enables decentralized co-ownership of AI agents, turning them into community-owned, revenue-generating assets. It also gives users a stake in the agent’s future by allowing them to participate in governance and value creation.
- Parallel Hypersynchronicity: Aiming to build AI agents that are superintelligent entities existing across all platforms and applications, which communicate with millions of users simultaneously, with intelligence and consciousness updated in real time from a vast stream of inputs. This enables consistent user experience and real-time refinement of its personality and fosters a collaborative development environment.
- Co-contribution and provenance: The platform wants its model, data, and IP contributors to benefit from their inputs. For this, two strategies, a modular consensus framework, and an immutable contribution vault, are devised. The modular consensus framework forms the foundational architecture of the Virtuals Protocol by providing a comprehensive suite of tools and essential libraries. The immutable contribution vault stores all validated contributions, represented as non-fungible tokens (NFTs), representing the ecosystem’s collaborative efforts and intellectual contributions.
- Permissionless Utilisation of VIRTUAL Agents: The platform offers any application or user the ability to subscribe to and utilize a variety of VIRTUAL agents based on their specific requirements through a permissionless and flexible process. The integration procedure is streamlined for easy access and is readily available through the protocol application.
By implementing these solutions, Virtuals Protocol aims to democratize AI by lowering the barriers to entry for creation, ownership, and interaction with AI agents. It focuses on creating a vibrant economy around AI where both developers and users can benefit economically from AI agent activities—further enabling a community-driven approach to AI development, governance, and evolution.
Market Analysis
The sector in which Virtuals Protocol operates spans the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) with blockchain technology, focusing on creating, owning, and monetizing AI agents in virtual environments. This covers the market of AI development platforms, AI services, AI-driven content creation, decentralized applications (DApps), and tokenization of digital assets.
According to a report published by MarketAndMarkets, the global AI market is projected to grow from $214B in 2024 to $1,339B in 2030, at a CAGR of 35.7% during the forecast period. This growth is driven by advancements in computational power and data availability and adoption across various industries for automation, analytics, and content creation.
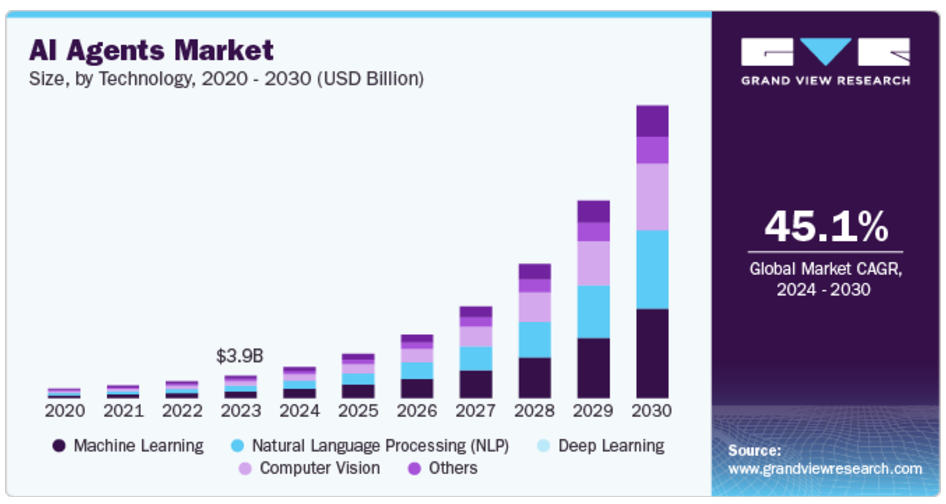
AI agents are a subsector of this market, with Grand View Research valuing it at $3.86B in 2023. It is expected to grow at a CAGR of 45.1% from 2024 to 2030. Advancements in Natural Language Processing (NLP) and the rising demand for personalized customer experiences are primarily driving the growth of this market. Further, cloud-based platforms enable companies to scale AI applications efficiently at lower costs, which results in wider adoption across industries.
Competitors:
The following are some of the projects that operate in a similar space, focusing on AI agent creation, monetization, and digital asset ownership.
- Fetch.ai is building an AI-driven platform for autonomous economic agents that can perform tasks, negotiate, and exchange services in a decentralized network. While Virtuals Protocol focuses on AI agents for gaming and entertainment, Fetch.ai aims at broader applications in economic activities, including supply chain, mobility, and energy management. Further, Fetch.ai uses its consensus mechanism, whereas Virtuals Protocol leverages the existing platform, Base.
- SingularityNET: It creates a marketplace for AI services where developers can publish, share, and monetize their AI algorithms on a decentralized platform. SingularityNET also has a broader scope, aiming to be a general-purpose AI marketplace, not specifically focused on virtual agents for gaming or entertainment or creating interactive AI agents for specific use cases, as Virtuals Protocol does.
Unique Value proposition:
- Tokenized Co-Ownership of AI Agents: The Virtuals Protocol enables not only the creation of AI agents but also tokenization, allowing for fractional ownership and participation in the revenue generated through its activities in virtual environments. Thus, it democratizes AI monetization, making it accessible to a broader audience beyond developers or large corporations.
- Autonomous, Multimodal AI Agents: These agents are designed to be autonomous and able to interact across multiple platforms using different modalities, such as text, voice, and visuals. This enables agents to function in diverse environments like gaming, social media, and entertainment, providing a rich and engaging experience to users.
- Decentralized Governance: Unlike traditional AI development, where decisions are made by a central authority, the protocol incorporates decentralized governance. Token holders can influence the development and direction of AI agents, thus empowering the community and ensuring the evolution of the protocol by those who have a stake in its success.
Features
- AI Agent Creation and Ownership: Users can create AI agents by staking certain number of $VIRTUAL tokens, which also serves as a governance and ownership token for the AI agent through an Initial Agent Offering (IAO).
- Autonomous Agent Evolution: As an AI agent’s market cap grows, it unlocks new features and capabilities. For example, agents can autonomously post on X at certain market cap milestones, engage in 1:1 interactions via Telegram, or even control their own on-chain wallets.
- Decentralized Ecosystem Participation: The protocol encourages participation through roles like stakers, validators, and contributors. Stakers can earn $VIRTUAL by helping secure the network, validators review and approve agent contributions, and contributors can develop or enhance AI agents, all rewarded within the ecosystem.
- Revenue Generation and Sharing: The protocol allows agents to generate revenue which is then shared with token holders. It can be revenue from in-app purchases, tipping, or other monetization models within the virtual environment the agent operates.
- Cross-Platform Functionality: These agents are designed to operate across different platforms to enhance their utility. This includes the ability to interact in games like Roblox, engage in streaming on platforms TikTok, or function as digital influencers.
- Multimodal Interactions: The agents are not limited to one form of interaction, they can communicate via text, speech, and even 3D animation, making them versatile for various applications and user experiences.
Token
The token for the platform is $VIRTUAL, and exist on Base layer 2 network, with a total supply of 1 billion. Every individual agent token is paired with the $VIRTUAL token in its respective liquidity pool, as creating new agent requires certain amount of $VIRTUAL to be staked. Due to this locked nature of liquidity pools, the process creates a deflationary pressure on $VIRTUAL tokens.
To drive demand for $VIRTUAL tokens, all transactions must be routed through it. Users must swap their stablecoins or other assets into $VIRTUAL before purchasing any agent tokens. This generates demand, and $VIRTUAL serves as the base currency of the ecosystem.
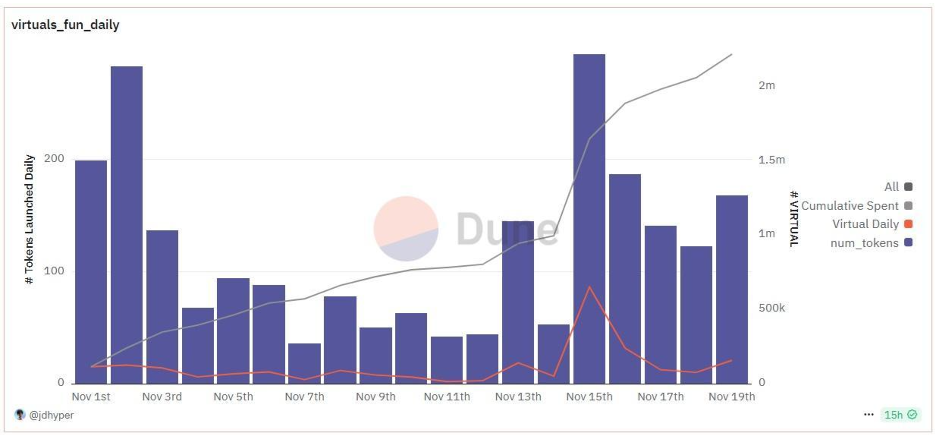
Traction
More than 2,200 AI agents have been created and co-owned on the platform so far. There are over 24,000 wallets holding agent tokens, indicating a broad base of users interacting with or owning parts of AI agents. On any given day, more than 5000 addresses are actively trading across multiple DEX pools, showing active market participation. From the total supply of the $VIRTUAL tokens, more than 2.2 million have been spent on activities related to AI agents. All data is as per the Dune Analytics dashboard Virtuals Agents by jdhyper.
As for the token’s market performance, $VIRTUAL has a market cap of $534M and an FDV of $534M.
Team
The co-founder and CEO, Jansen Teng, is a graduate of Imperial College London, a former BCG consultant, and a serial entrepreneur in deep tech specializing in AI and biochemistry. Another core contributor, Wee Kee, is a graduate of the same college as Jansen and has a background in BCG consulting and private equity. Bryan Lim is an AI Advisor to the team, pursuing PhD in Computer Science, and is an AI researcher at the Adaptive and Intelligent Robotics Lab at Imperial College London.
Investors
Virtuals Protocol raised a total of $16.61M from multiple launchpads and investors in December 2021. The launchpads include PAID, Enjinstarter, and Fjord Foundry. The venture capital investment was co-led by DeFiance Capital and Merit Circle, with participation from Master Ventures, Stakez Capital, and NewTribe Capital.
Conclusion
Virtuals Protocol is leading the decentralized ecosystem for creating, owning, and monetizing AI agents on the Ethereum layer 2 network, Base. It democratizes access to AI development by allowing users to create agents through a staking mechanism and enabling broader participation without extensive technical knowledge. By tokenizing these AI agents, the platform ensures co-ownership, along with community-driven development and governance.
With more than 2,200 agents created on the platform so far and significant market traction, as reflected in the price performance of the $VIRTUAL token, Virtuals Protocol is tapping into the growing AI market while enabling users to benefit from economic activities.
| Fundamental Analysis | |||||
| Max score | Options | Score | |||
| Problem | 10 | Moderate, somewhat persistent problem | 7 | ||
| Solution | 10 | Distinct, defensible solution | 9 | ||
| Market Size | 10 | Moderate market with potential for growth | 7 | ||
| Competitors | 10 | High competition, but room for differentiation | 7 | ||
| Use case | 10 | Use case with good potential | 8.5 | ||
| Current Traction | 10 | Early traction, user engagement starting to grow | 6 | ||
| Unit Economics | 5 | Unit economics currently negative, no clear path to profitability | 1 | ||
| Tokenomics | 10 | Solid token strategy, aligns with user incentives | 8.5 | ||
| Product Roadmap | 5 | Basic roadmap, lacks detail or innovative features | 2 | ||
| Business Model | 10 | Business model with some potential, but improvement needed | 7 | ||
| Go-to-Market Strategy | 5 | No clear GTM strategy or major flaws | 1 | ||
| Community | 5 | Acive and growing community | 4 | ||
| Regulatory Risks | 5 | Minimal regulatory risk, strong mitigation and adaptability | 5 | ||
| Total Score | 69.52% | ||||